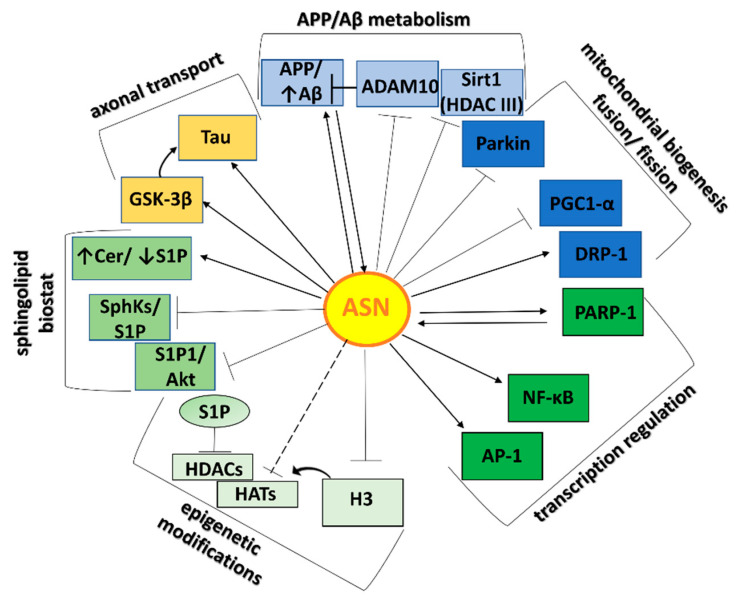
Figure 2.
Toxic ASN-protein network and its effect on biological processes. The influence of ASN on individual proteins is marked with arrows that terminate with → (activation), or ┴ (inhibition/deterioration). A dashed line between ASN and HATs and a little arrow from H3 to HATs/HDACs mean that ASN inhibits histone acetylation by directly associating with histone H3, which masks residues required for acetylation [28]. Therefore indirectly, ASN can perturb the HATs/HDACs balance on the side of acetylation inhibition. Proteins interacting with ASNs have been grouped and color coded into categories depending on their biological function. Abbreviations: ASN—alpha-synuclein; APP/Aβ—amyloid-beta precursor protein/amyloid-beta; Sirt1 (HDAC III)—silence information regulator 1-sirtuin 1 (histone deacetylases class III); ADAM10—a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain-containing protein 10, acting as alpha-secretase; parkin—E3 ubiquitin ligase; PGC-1α—peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-coactivator 1-alpha; Drp-1-dynamin-related protein 1; PARP-1—poly(adenosine 5′-diphosphate–ribose) polymerase-1; AP-1- activator protein 1, NF-κB—nuclear factor kappa B; H3—histone H3; HATs/HDACs—histone acetyltransferases/histone deacetylases; GSK-3β—glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; Tau—microtubule-associated protein; Cer—ceramide; S1P—sphingosine-1-phosphate; SphKs—sphingosine kinases Note that sphingosine kinases were abbreviated as Sphks. However, ASN downregulates the Sphk1 [31], while inhibition of HDACs concerns the S1P synthesized by Sphk2 isoform.