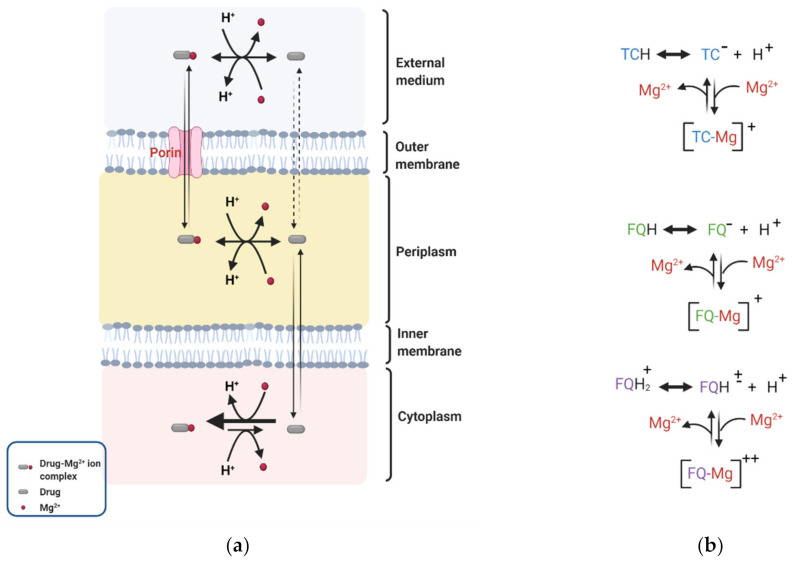
Figure 2.
Donnan potential (DP) across the OM of Gram-negative bacteria drives the periplasmic accumulation of antibiotics such as tetracyclines (TC) and fluoroquinolones (FQ). (a) TC or FQ permeates the OM complexed with Mg2+, becomes protonated in the periplasmic and loses its Mg2+ to a neutral form and crosses into the cytoplasm, where it is deprotonated and complexed with Mg2+ again. (b) A notable difference between FQ and TC is that some zwitterionic fluoroquinolones [FQH]± permeate the OM as fluoroquinolone-divalent ion complexes [FQ-Mg]++. Figures were created with BioRender.com.