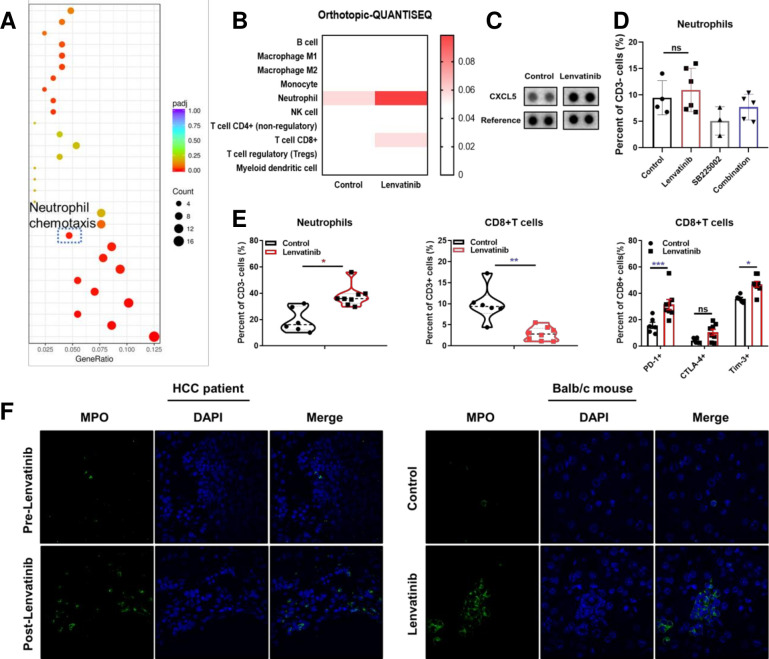
Figure 1.
The effect of lenvatinib on chemokines and recruitment of neutrophils. Gene ontology analysis for pathways regulated following treatment with lenvatinib versus control in subcutaneous BALB/c mice models assessed by RNA-seq (A). Immune infiltration estimations by timer for expression profiles tested by RNA-Seq data of orthotopic Hepa1-6 models (B). Proteome profiler mice XL cytokine array analysis for peripheral blood following treatment with lenvatinib versus control in BALB/c mice models (C). Histogram showing the effect of lenvatinib monotherapy, SB225002 and lenvatinib in combination with SB225002 on neutrophil recruitment (D). Scatter plots showing the infiltration of neutrophils, CD8+T cells and expression of PD-1, CTLA-4 and Tim-3 on CD8 +T cells in orthotopic BALB/c mice models (E). Representative immunofluorescence staining images showing infiltration of MPO+ cells in biopsy samples of HCC patients before and after lenvatinib treatment (left, 60×) and in tissue samples of orthotopic BALB/c mice models following treatment with lenvatinib versus control (right. 100×) (F). *P<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; ns, not significant; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; RNA-Seq, RNA sequencing.