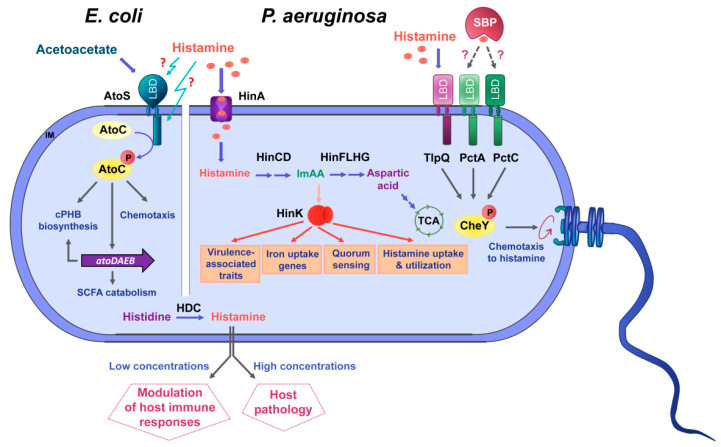
Figure 4.
Summary of data available on histamine sensing and secretion by bacteria. On the left, histamine sensing by the TCS AtoSC in E. coli. On the right, histamine assimilation and chemotaxis in P. aeruginosa. Lower part: Many bacteria synthesize histamine by a decarboxylation of histidine using the histidine decarboxylase (HDC) and secrete histamine. Blue arrows: metabolic pathways; orange arrows: gene expression regulation; grey arrows: activation of biological processes; dotted lines: hypothetical interaction; LBD: ligand-binding domain; SBP: solute-binding protein; ImAA: imidazole-4-acetic acid; HinA: permease for the histamine uptake; HinCD: enzymes for the conversion of histamine to ImAA; HinFLHG: enzymes for the conversion of ImAA to aspartic acid; HinK: LysR-family response regulator; IM: inner membrane.