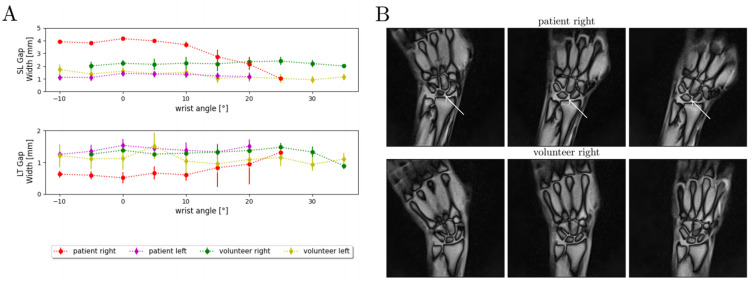
Figure 7.
Quantitative and qualitative changes in carpal configurations in a patient with a partial scapholunate ligament rupture and a gender- and size-matched healthy volunteer during active radioulnar movement. (A) SL and LT gap widths are given as a function of wrist angle across the range-of-motion. The gap widths are indicated as means (dots) and standard deviations (whiskers). A total of 300 MR images per wrist were analyzed and quantified by our framework. Indicated are the measured SL and LT gap widths of the wrist-injured patient (partial SL ligament rupture, “patient right”, red), the contralateral wrist (“patient left”, purple), and the corresponding wrists of the matched and healthy volunteer (“volunteer right”, green; “volunteer left”, yellow). For the sake of visualization, the wrist angles are grouped at intervals of 5°. (B) Three exemplary MR images are shown for the patient and the volunteer at various positions throughout the active radioulnar movement range. The increased dehiscence of the SL gap of the injured wrist (white arrows) is particularly obvious in the neutral position and ulnar abduction and at the proximal portion of the SL gap.