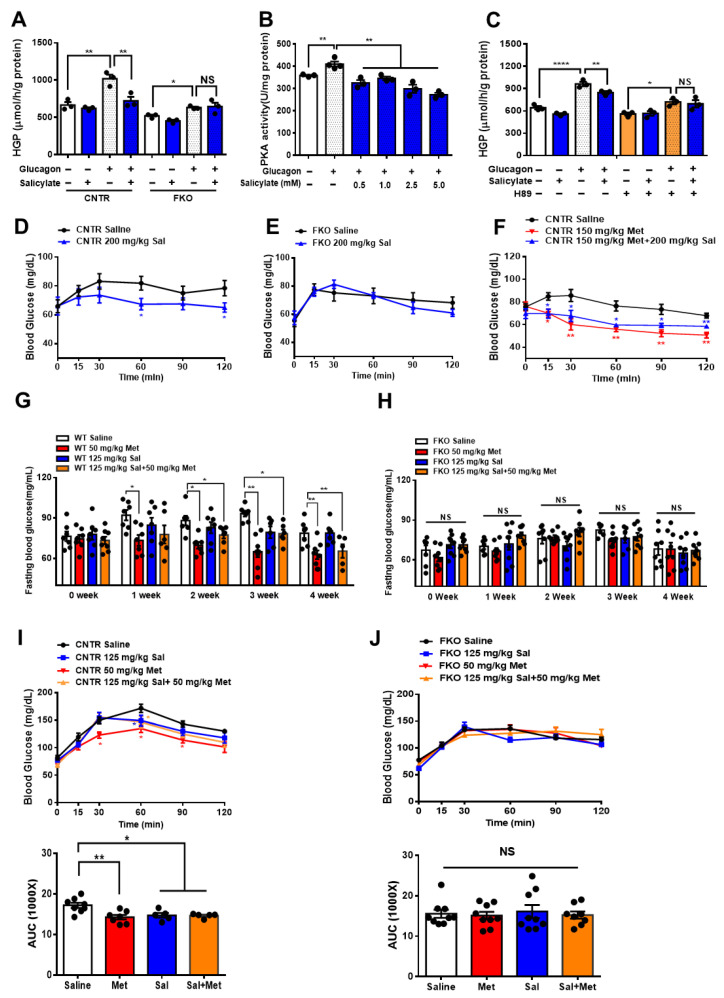
Figure 5.
Salicylate suppresses glucagon-induced HGP through the PKA–Foxo1 signaling pathway in hepatocytes and has no improvement on metformin action on glucose homeostasis. (A) Primary hepatocytes isolated from control and FKO mice were pretreated with 0.5 mM of salicylate for 30 min and treated with 100 nM of glucagon for 3 h. Glucose content was measured, n = 3 independent experiments/group. (B) Control primary hepatocytes were pretreated with 0.5, 1, 2.5, and 5 mM of salicylate for 30 min, followed by 100 nM treatment for 1 h. PKA activity was measured, n = 3–4. (C) Control hepatocytes were pretreated with H89 and 0.5 mM of salicylate, followed by 100 nM glucagon treatment for 3 h. Glucose content was measured, n = 3 independent experiments/group. (D,E) Control (D) and FKO (E) mice were i.p. injected with 200 mg/kg body weight salicylate (Sal) after 16 h fasting. Blood glucose was monitored at indicated time points, n = 5–9 mice/group. (F) Control mice were i.p. injected with 150 mg/kg body weight metformin (Met) or 150 mg/kg body weight metformin (Met) + 200 mg/kg body weight salicylate (Sal) after 16 h fasting. Blood glucose was measured at indicated time points, n = 5–6 mice/group. (G,H) Control (G) and FKO (H) mice were administered with 50 mg/kg body weight metformin (Met), 125 mg/kg body weight salicylate (Sal), or 50 mg/kg body weight Met + 125 mg/kg body weight Sal via oral injection. Blood glucose was monitored after 16 h fasting, n = 5–8 mice/group. (I,J) Pyruvate tolerance test in control (I) and FKO (J) mice administered with 50 mg/kg body weight metformin (Met), 125 mg/kg body weight salicylate (Sal), or 50 mg/kg body weight Met + 125 mg/kg body weight Sal via oral injection, n = 5–8 mice/group. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p <0.0001, NS: no significance, CNTR: control.