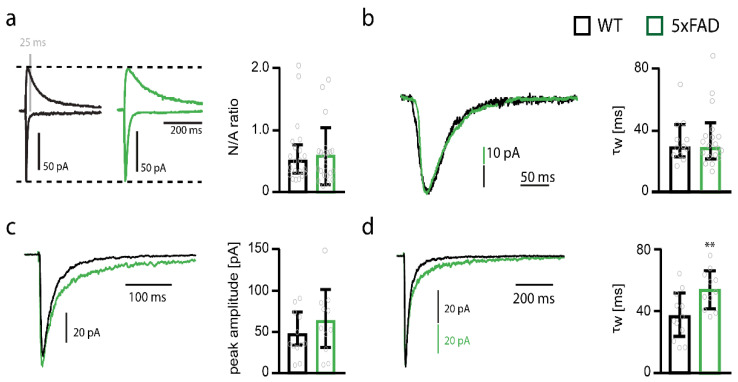
Figure 2.
Deactivation time constant of extrasynaptic NMDAR currents increases in somatosensory cortex pyramidal cells of 5xFAD mice. (a) Example traces of NMDAR and AMPAR-mediated currents and bar graph of the NMDA/AMPA ratios (N/A ratios) of pyramidal cells from wildtype (WT) (black, n = 21) and 5xFAD (green, n = 22) mice. (b) Example traces and bar graph of the decay weighted tau (τw) of NMDAR-mediated currents of pyramidal cells from WT (n = 12) and 5xFAD (n = 20) mice. (c) Example traces of extrasynaptic NMDAR-mediated currents recorded by ultra-fast application of glutamate onto nucleated patches obtained from somatosensory cortex pyramidal cells of WT (black) and 5xFAD (green) mice. Peak amplitudes (WT n = 12 vs. 5xFAD n = 11) of NMDAR-mediated currents are shown in the bar graph. (d) Example traces of normalized extrasynaptic NMDAR-mediated currents recorded by ultra-fast application of glutamate onto nucleated patches obtained from somatosensory cortex pyramidal cells of WT (black) and 5xFAD (green) mice. Weighted time constants (τw) of NMDAR-mediated current deactivation are shown in the bar graph (WT n = 12 vs. 5xFAD n = 11). Data in bar graphs are shown as median ± interquartile range. Empty grey circles depict single data points. t-test: ** p < 0.001.