Figure 5.
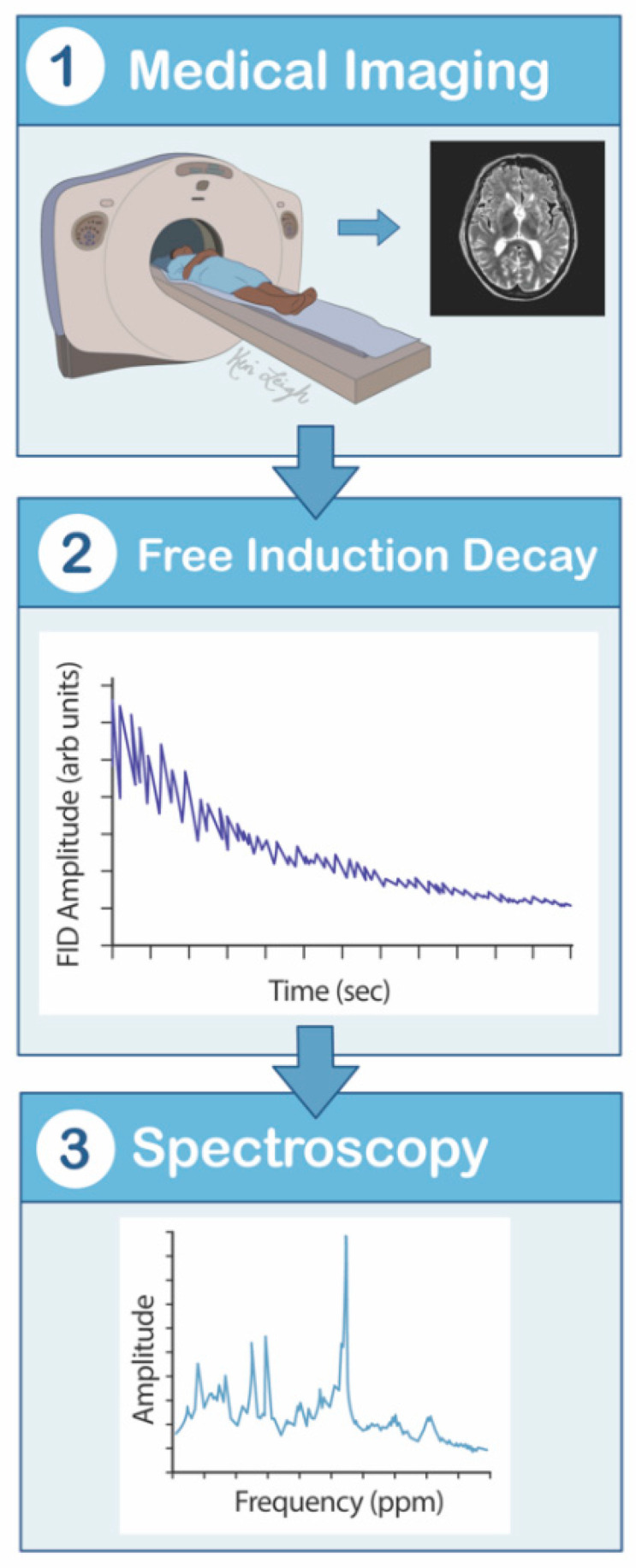
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy mechanism flowsheet. (1) The patient lies supine in the MRS scanner. (2) The hydrogen nuclei contain a nonzero intrinsic quantum mechanical spin of the protons and neutrons, which is manipulated by magnetic fields. Magnetization is applied, creating an observed nuclear magnetic resonance signal. Frequencies are then detected by a radiofrequency coil placed near the brain, creating a free induction decay. (3) The electromagnetic force that is generated is proportional to the magnitude of magnetization, and this proportion allows the MRS to provide spectra of the signal source. MRS is a magnetic resonance spectrum that graphically displays detected signals as a function of temporal frequencies. MRS—magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
