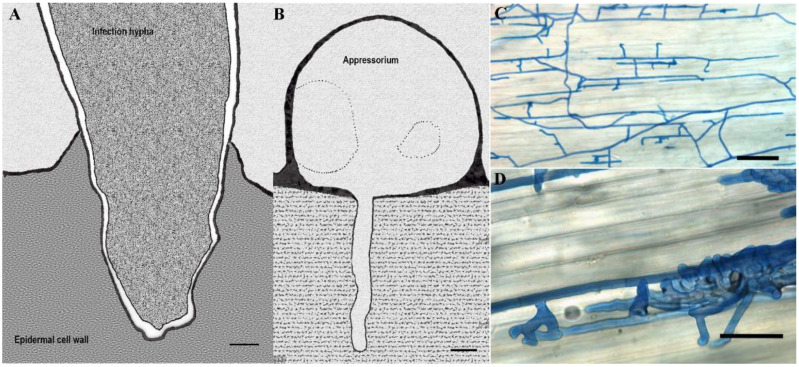
Figure 5.
Different infection structures of phytopathogenic fungi. (A) An infection hypha of Fusarium culmorum invading the epidermal cell wall of the lemma at 36 h after inoculation (hai) observed transmission electron microscope; (B) Transmission electron micrograph of Pyricularia grisea appressorium formed on cellophane membrane with the penetration peg invading the substratum; (C,D) Light microscopy of compound appressoria development of Rhizoctonia solani on cauliflower hypocotyls after trypan blue staining of hyphae. Bulbous foot structures branch from runner hyphae on the plant (C). Lobate appressoria and infection cushions consist of agglomerated and highly ramified hyphae (D). Scale bars: (A,B) = 1 μm; (C,D) = 100 μm. Pictures re-illustrated from: (A): [83], (B): [3], (C,D): reprinted with permission from Pannecoucque, J.; Höfte, M. Interactions between cauliflower and Rhizoctonia anastomosis groups with different levels of pathogenicity. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 1–12 [84].