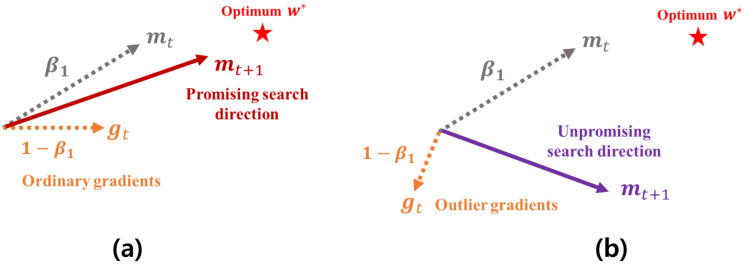
Figure 4.
The example to explain how the outlier gradient negatively affects a direction the first momentum. (a) shows an ideal case that the first momentum is computed by the current momentum and the ordinary gradient. In this case, the first momentum becomes further close to the optimal weight. On the other hands, (b) shows a bad case that the first momentum is distorted by the unpromising (i.e., unexpected outlier) gradient. In this case, its next search direction moves away from the optimal weight by the unpromising gradient.