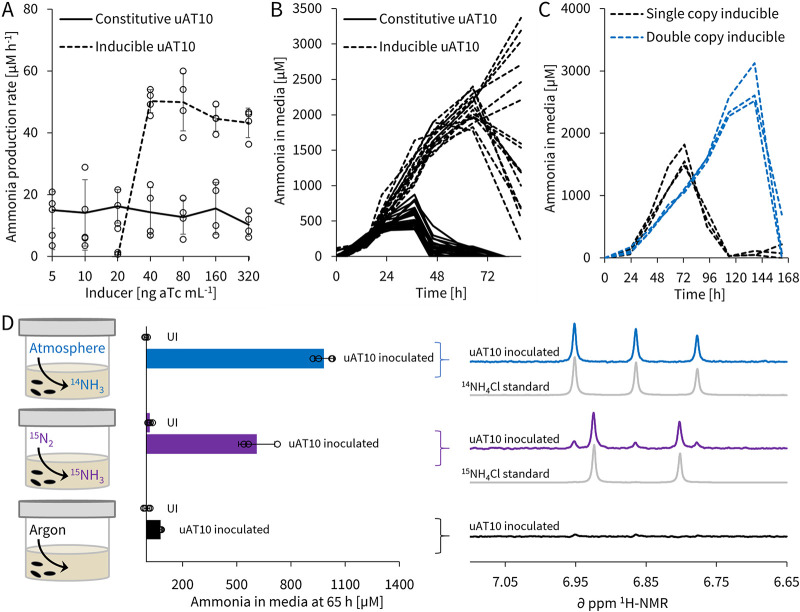
FIG 3.
uAT-driven ammonia production is from de novo nitrogen fixation and can be inducibly controlled, and circuit stability is further improved through multicopy redundancy. (A) Average ammonia production rates of A. brasilense ΔglnE between 15 and 35 h with constitutive and inducible expression of uAT10 at different anhydrotetracycline (aTc) inducer concentrations. (B) Individual time course data, with inducible off-state (below 40 ng ml−1 aTc) lines omitted for clarity (see Fig. S12 for full data). (C) Time course data comparing on-state ammonia production of single- and double-copy uAT10 in A. brasilense ΔglnE at 200 ng aTc ml−1. (D) Controlled atmosphere labeling study of the inducible uAT10 circuit in A. brasilense ΔglnE: medium ammonia concentrations were first determined by the indophenol colorimetric assay 65 h postinduction (200 ng ml−1 aTc) and then analyzed by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) using an ammonia-selective pulse sequence. All cells were inoculated in semisolid NFbHP medium at OD600 of 0.1 and ammonia concentrations were determined by the indophenol method (see Fig. S4 for assay). UI, uninoculated controls. Error bars show standard deviations for biological quadruplicates (A) and triplicates (D). See Fig. S21 for genetic circuit diagrams and parts; the constitutive circuit used was R2, the single copy inducible circuit was J3, and the double-copy inducible circuit was V2, all on pTS7.