FIG 2.
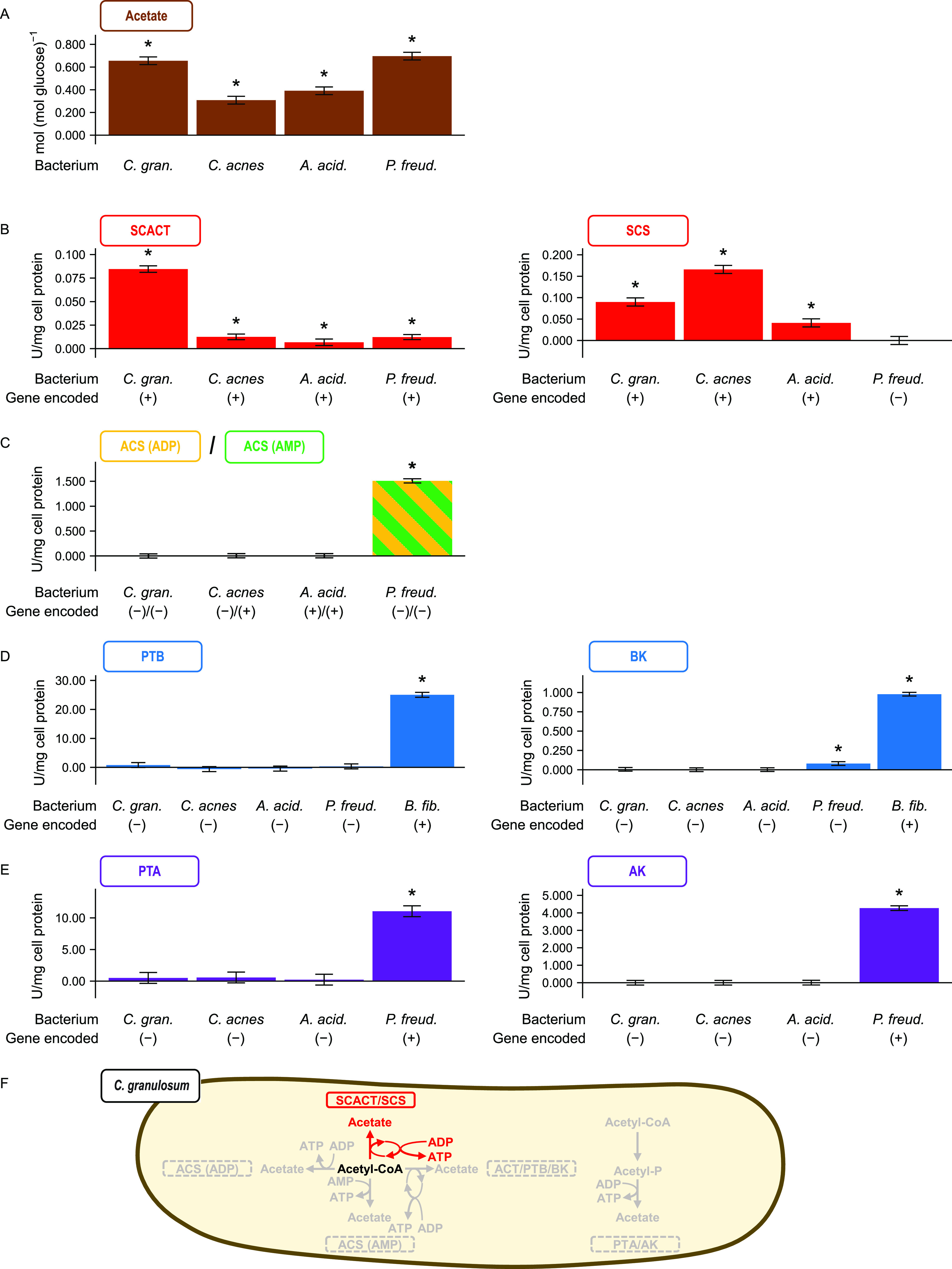
The bacterium Cutibacterium granulosum forms acetate using the SCACT/SCS pathway. Other propionibacteria are included for comparison. (A) Acetate formed during glucose fermentation. (B to E) Activity of enzymes in different pathways for forming acetate. (F) Summary of pathways in C. granulosum. In panel C, the assay cannot distinguish between the enzymes of the ACS (ADP) and ACS (AMP) pathways. In panel D, a nonpropionibacterium (Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens) was included as a control. No attempt was made to measure the activity of BCACT in the BCACT/PTB/BK pathway. Results are means ± standard errors for at least 3 biological replicates (batches of cell extract prepared from independent cultures). Means different from 0 (P < 0.05) are marked with an asterisk. Abbreviations: ACS (ADP), acetyl-CoA synthetase (ADP forming); ACS (AMP), acetyl-CoA synthetase; AK, acetate kinase; BCACT, butyryl-CoA:acetate CoA-transferase; BK, butyrate kinase; PTA, phosphotransacetylase; PTB, phosphotransbutyrylase; SCACT, succinyl-CoA:acetate CoA-transferase; SCS, succinyl-CoA synthetase (ADP-forming); A. acid., Acidipropionibacterium acidipropionici; C. acnes, Cutibacterium acnes; C. gran., Cutibacterium granulosum; P. freud, Propionibacterium freudenreichii.
