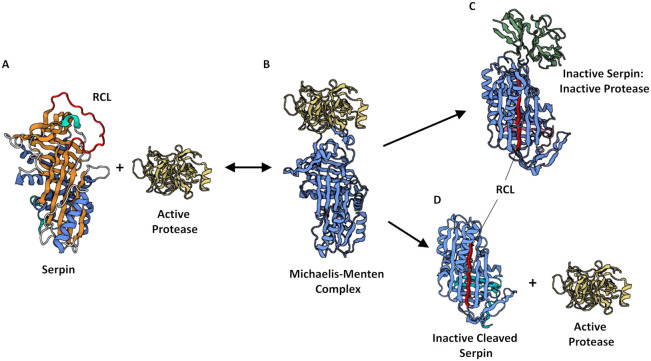
Figure 2.
The inhibitory or alternative substrate mechanisms of serpin-protease interaction. (A) The metastable native serpin exists with its reactive centre loop (RCL) exposed as a pseudo-substrate for its target protease (PDB code: 1QLP). (B) The target protease binds to the P1 site located on the RCL forming a Michaelis-Menten complex (PDB code: 1OPH). (C) The target protease cleaves the target scissile bond inducing a dramatic conformational shift in the serpin resulting in the formation of a covalent serpin-protease complex where the RCL is pulled down into the centre of the serpin molecule and incorporated into β-sheet A, subsequently trapping and inactivating the covalently bound target protease (PDB code: 1EZX). (D) The “substrate” pathway will be favoured if the reaction does not occur rapidly enough. The protease escapes the conformational trap resulting in an inactive cleaved serpin and a free active protease (PDB code: 7API). PDB code 1QLP was accessed on 25 March 2021; 1OPH, 1EZX and 7API were accessed on 21 April 2021. Created with BioRender.com.