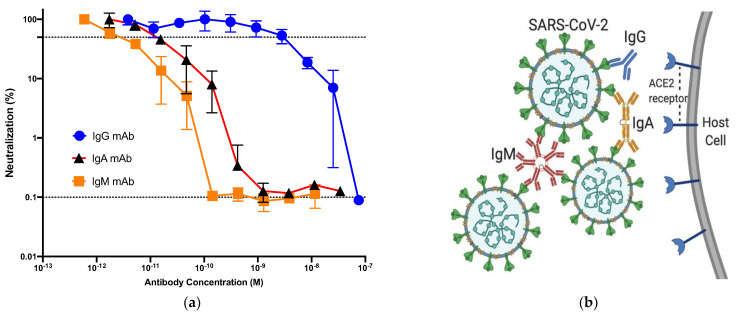
Figure 1.
(a) Neutralization of pseudo-typed lentivirus coated with the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein (LpVspike(+)) by anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). After pre-incubating LpVspike(+) with each anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing mAb at a 100 TCID50 (50% tissue culture infectious dose), the mAb/virus mixtures were added to ACE2-expressing CRFK cells and cultured for 48 h, after which luciferase activity was measured. The IgG, IgM, and IgA mAbs were diluted serially three-fold, from an initial concentration of 10 μg mL−1 to 0.016 μg mL−1. The x- and y-axes are depicted in logarithmic scale [18]. (b) Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by three anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing mAbs (IgG, IgM, and IgA). IgG has two antigen-binding sites, while dimeric IgA has four antigen-binding sites. Pentameric IgM has 10 antigen-binding sites and can bind 10 small antigens; however, due to steric restrictions, only five large viral antigens can be bound by one IgM molecule. IgG can bind to only one large antigen, whereas dimeric, trimeric, and pentameric IgA can bind to multiple large antigens.