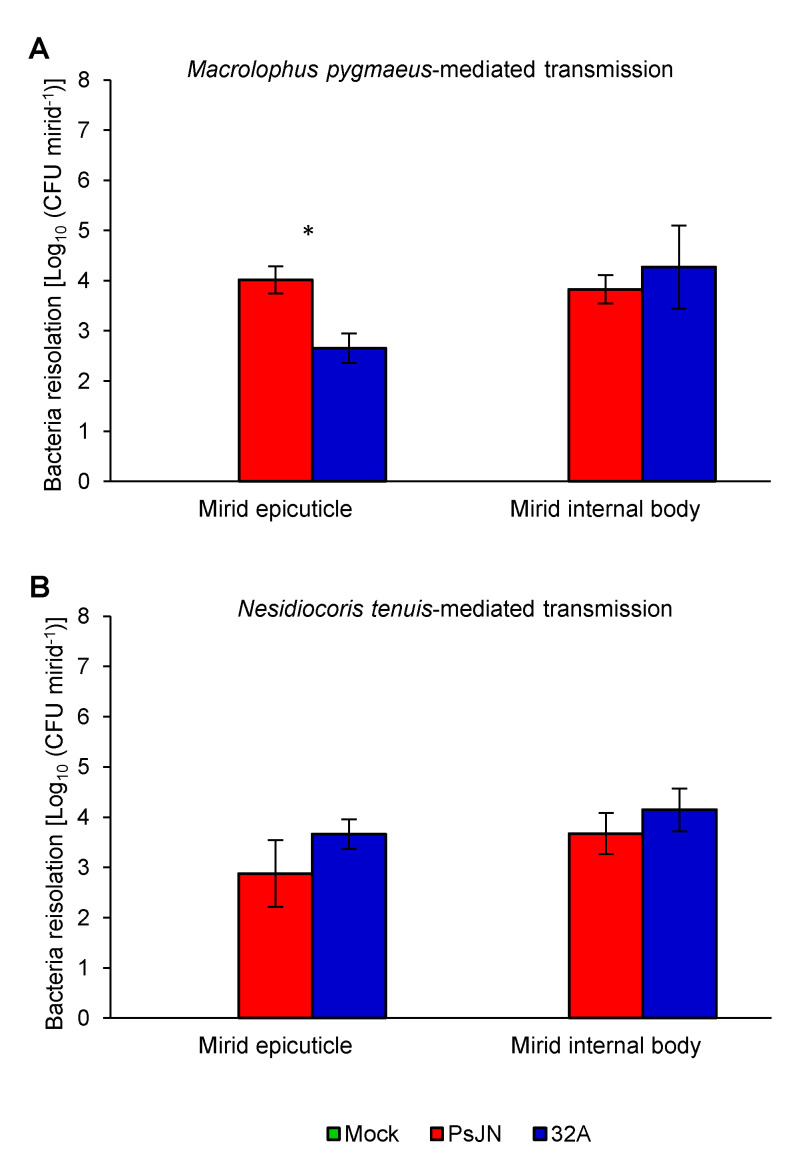
Figure 4.
Quantification of endophytic bacterial strains on the mirid epicuticle and internal body. Bacterial re-isolation was carried out from a mirid washing suspension to collect bacteria adhering to the mirid epicuticle or from tissue grinding of surface-disinfected mirids to collect bacteria in the mirid internal body at the end of the mirid-mediated transmission (Day 14) with Macrolophus pygmaeus (A) or Nesidiocoris tenuis (B). The quantity of re-isolated bacteria is expressed as the colony forming units per mirid (CFU mirid−1) fed on mock-inoculated plants (Mock, green) and plants inoculated with Paraburkholderia phytofirmans PsJN (PsJN, red) or Enterobacter sp. 32A (32A, blue). The two-way analysis of variance showed no significant differences between the two experimental repetitions (p > 0.05) and data from the two experiments were pooled. Mean and standard error values for positive samples and at least nine replicates (mirids) are presented for each treatment. Asterisks indicate significant differences in the pairwise comparisons between the PsJN- and 32A-inoculated samples, according to the Mann–Whitney test (p ≤ 0.05). Neither PsJN nor 32A bacterial colonies were isolated from mirids fed on the mock-inoculated plants.