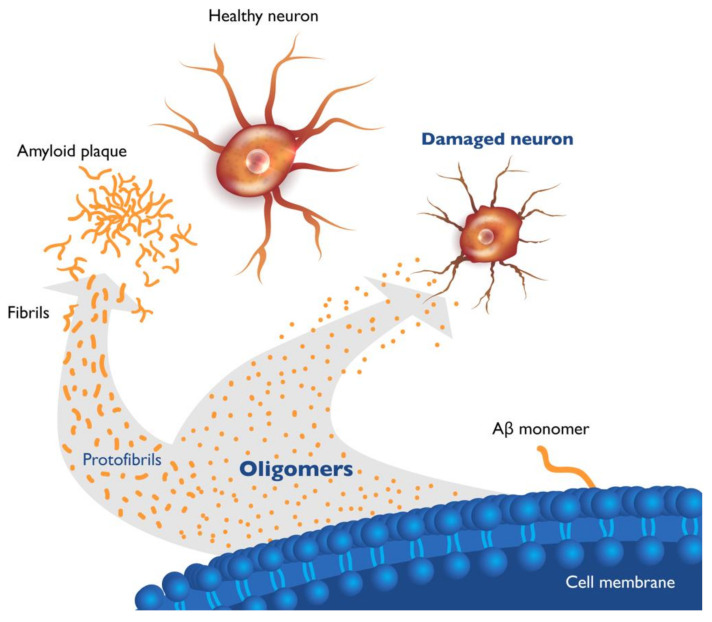
Figure 1.
Beta amyloid species in brains of Alzheimer’s patients. Cleavage of amyloid precursor protein in neuronal membranes produces amyloid monomers. Misfolded beta amyloid (Aβ) monomers aggregate into soluble oligomers of various lengths (dimers to dodecamers) and soluble protofibrils (large oligomers). Oligomers further aggregate into insoluble fibrils and plaque. Soluble Aβ oligomers, which are highly toxic to neurons and synapses, are considered upstream triggers of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathology.