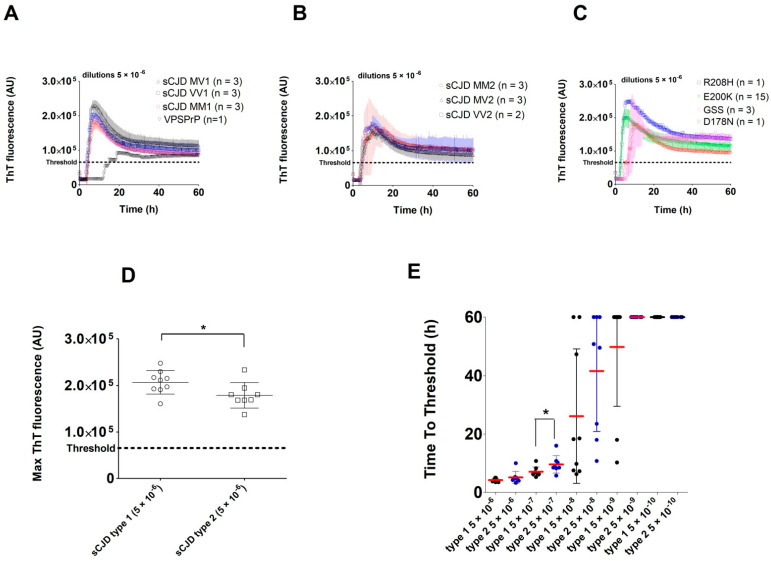
Figure 2.
RT-QuIC analysis of archived brain homogenates of patients with sporadic and genetic prion diseases: (A) Kinetics of RT-QuIC reaction comparing samples of sCJD type 1 group (MM, VV and MV) and Variably Protease Sensitive Prionopathy case (VPSPrP) BHs (dilution 5 × 10−6). The VPSPrP sample had notably lower max ThT fluorescence and longer time to threshold; (B) Kinetics of RT-QuIC reaction comparing samples of sCJD type 2. group (MM, VV, and MV) BHs (dilution 5 × 10−6). One case of sCJD VV2 gave a negative result and was omitted from the mean calculation; (C) Kinetics of RT-QuIC reaction in the group of genetic prion diseases (gCJD E200K cases, R208H, D178N) and results of GSS BH samples. Kinetics of GSS BHs showed increased variability of max ThT fluorescence and time to threshold; (D) Comparison of max ThT fluorescence values of sCJD type 1 and 2 BHs diluted 5 × 10−6 (* p < 0.05); (E) Comparison of time to threshold values between groups of sCJD type 1 and 2 BHs (* p < 0.05). Arithmetic mean values with standard deviation are shown. A time of 60 h was assigned when the threshold was not reached.