Figure-2: Delayed treatment with CTLA4-Ig plus Bortezomib inhibits established primary humoral responses in mice immunized with donor spleen cells.
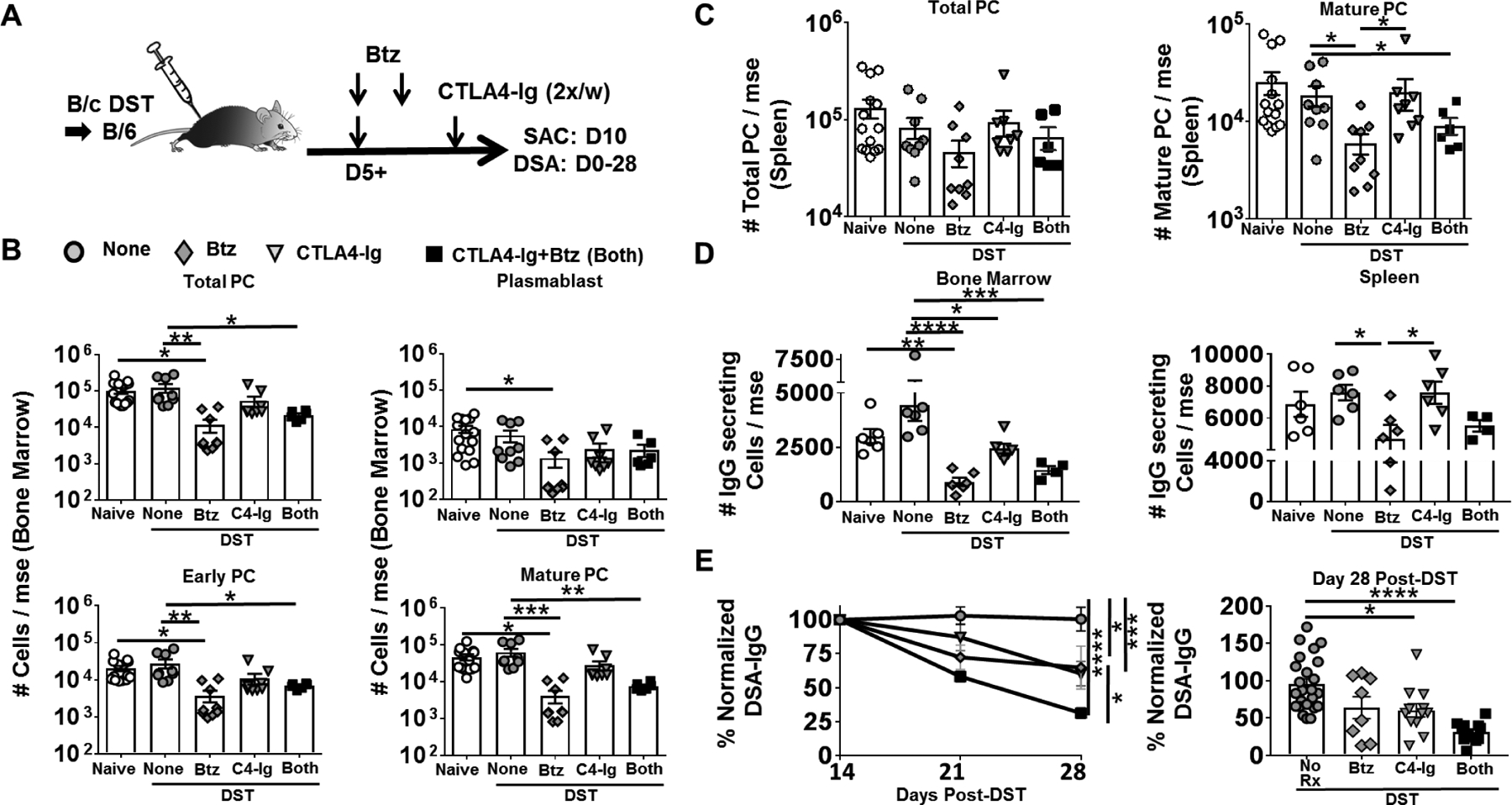
(A) Experimental design. C57BL/6 mice were immunized with BALB/c donor splenocytes (DST) and received no treatment (None), CTLA4-Ig (C4-Ig; from D5), Bortezomib (Btz; D5, D6) or CTLA4-Ig and Bortezomib (Both; from D5). (B) Quantification of plasma cell (PC) subsets in bone marrow; (C) and spleen harvested from naïve or D10 post-DST. (D) Total IgG secreting cells in the bone marrow (Left) and spleen (Right), harvested from naïve or D10 post-DST. Y-axis represents total cells retrieved per mouse, not receiving (None) or receiving CTLA4-Ig (POD 5+) or Bortezomib (D5, 6) or Both (N=5–8/group). (E) Anti-BALB/c IgG were assessed from D14–28 after DST immunization (Left panel) (N=6–25/group), and effectiveness of mono or combination therapy were compared on D28 post-DST (Right panel) (N=8–25/group). Each dot represents an individual mouse, pooled from >2 independent experiments. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM and statistically significant differences assessed by one way ANOVA. (*P <0.05) (**P <0.01) (***P <0.001) (****P <0.0001).
