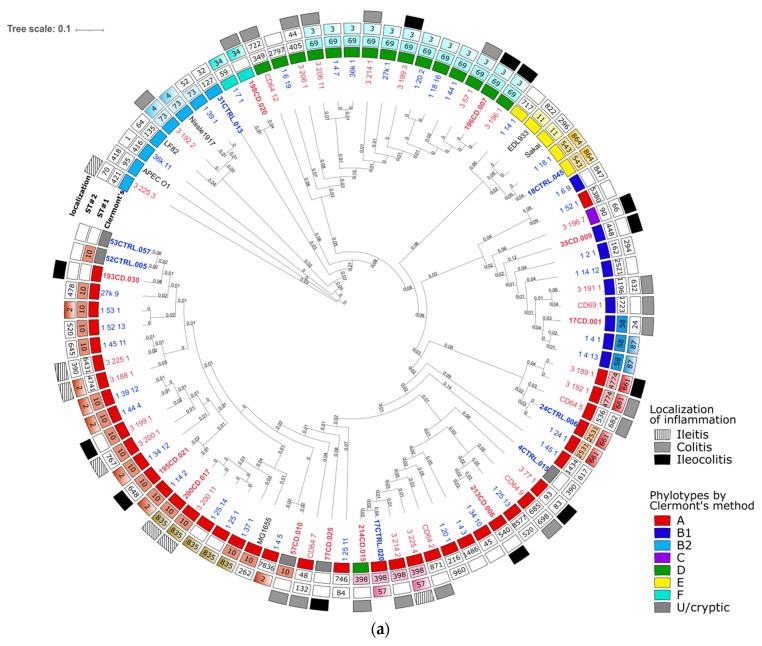
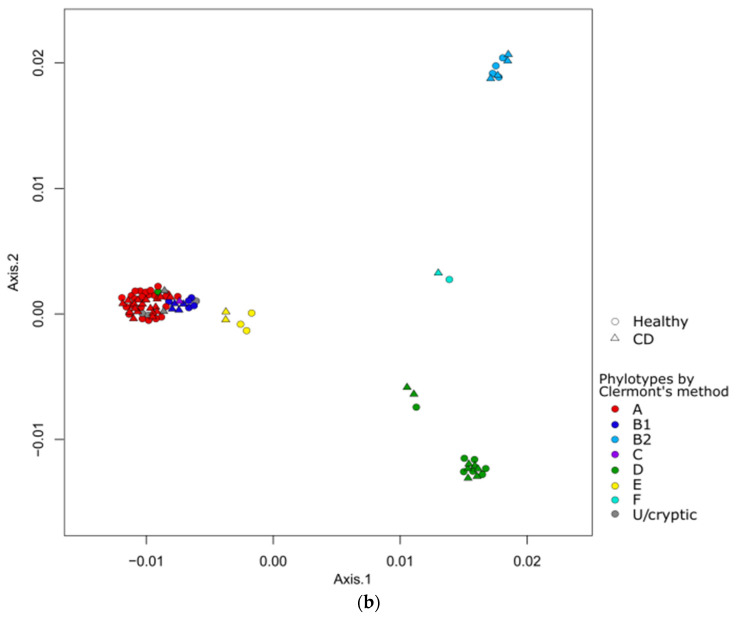
Figure 1.
Comparative genome analysis of fecal E. coli strains isolated from patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and healthy individuals. (a) Phylogenetic tree of 63 E. coli genomes and 18 MAGs (marked in bold) from healthy individuals (blue) and CD patients (red). Complete genomes of E. coli strains APEC O1, LF82, Sakai, EDL933, Nissle 1917, and K-12 substr. MG1655 were used as reference sequences (black). Phylogenetic groups by Clermont’s method [20] are highlighted on the inner ring. Sequence types (ST) by the Achtman’s scheme [49] and the Pasteur’s scheme [50] are marked as ST#1 and ST#2, respectively. Repeating STs are colored; (b) Multidimensional scaling (MDS) on average nucleotide identity (ANI) distance of all genomes is colored according to Clermont’s phylogroups.