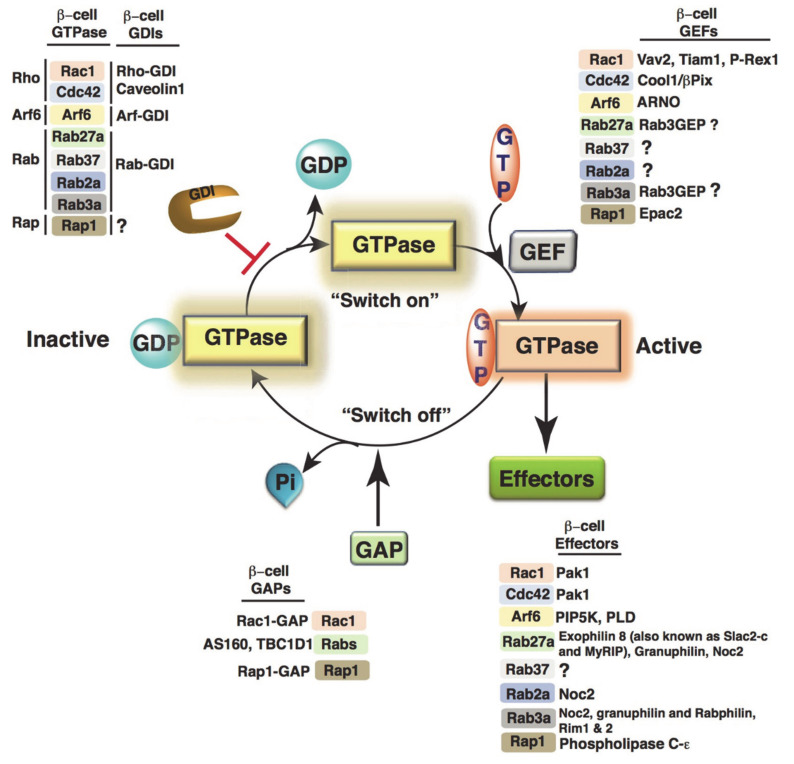
Figure 3.
Molecular switch mechanism of GTPases. In resting cells, GTPases are bound to an inhibitory protein GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) in an inactive GDP-bound form. Upon stimulation, guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) facilitate the conversion of inactive GTPases to the active GTP-bound form. The active GTPase then interacts with the effector proteins to propagate the downstream signals. GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) stimulate GTP hydrolysis from the active to inactive GTPase. The individual GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs relevant to islet β-cell signaling are listed with each GTPase.