FIGURE 1.
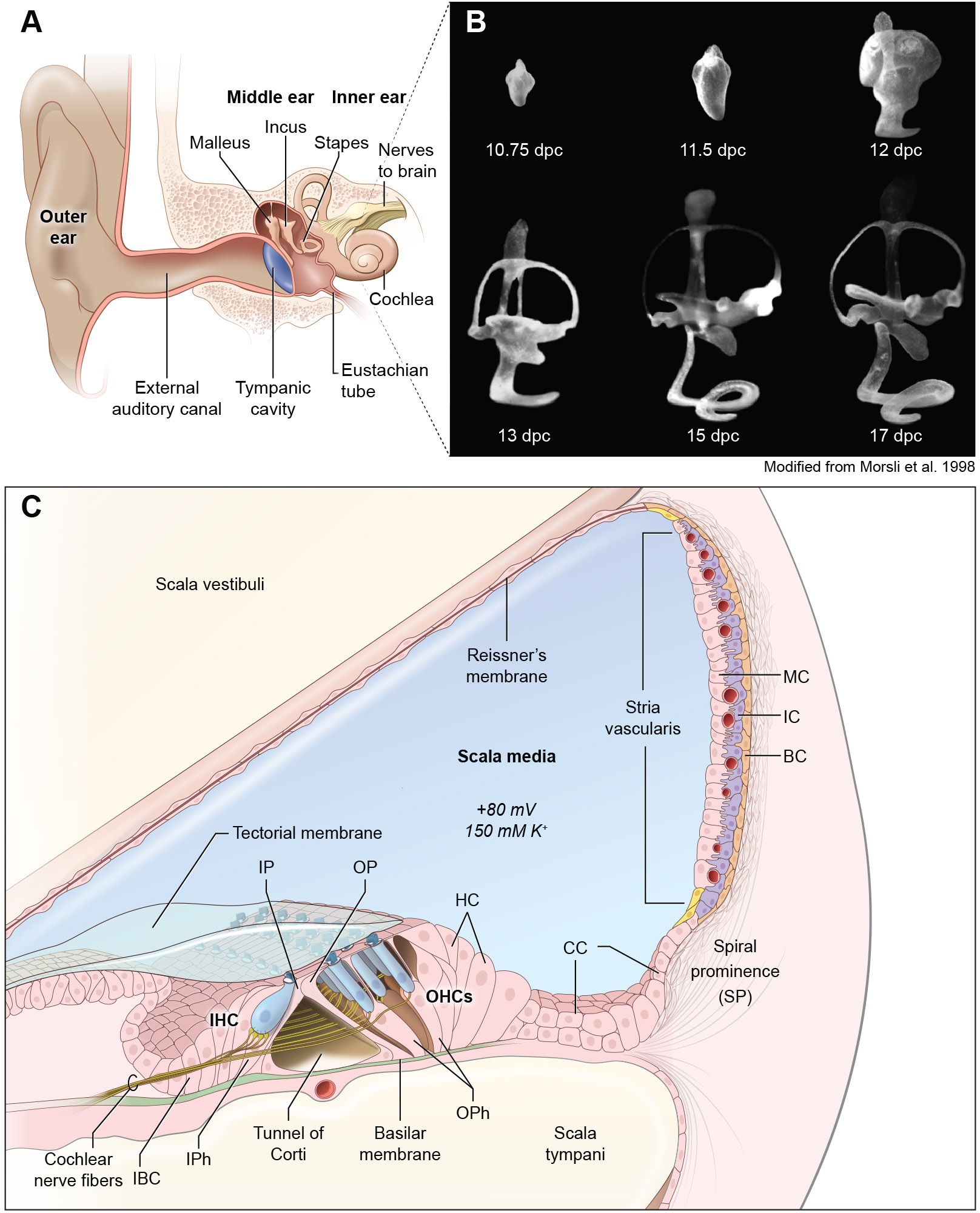
Development and structure of the ear. (A) Structure of the human ear showing its three main parts, outer, middle and inner ear. (B) Paint-filled mouse membranous labyrinths at embryonic days 10.75 days-postcoitum to postnatal day 1 (P1). Lateral views are shown. Scale bar, 200 μm. (C) Diagram of a cross-section of the cochlea. The roof of the cochlear duct is formed by two layers of flattened cells comprising Reissner’s membrane, while the base is formed by the basilar membrane, which separate the cochlear duct (scala media) from the scala vestibuli and the scala tympani. The three rows of outer hair cells, one row of inner hair cells and different types of supporting cells and the stria vascularis are shown. IHC; Inner Hair Cells, OHC, Outer Hair Cells, IP, Inner Pillar cells, OP; Outer Pillar Cells, HC; Hensen’s Cells, CC; Claudius Cells, BC; Basal Cells, IC; Intermediate cells, MC; Marginal Cells, IBC; inner border cells.
