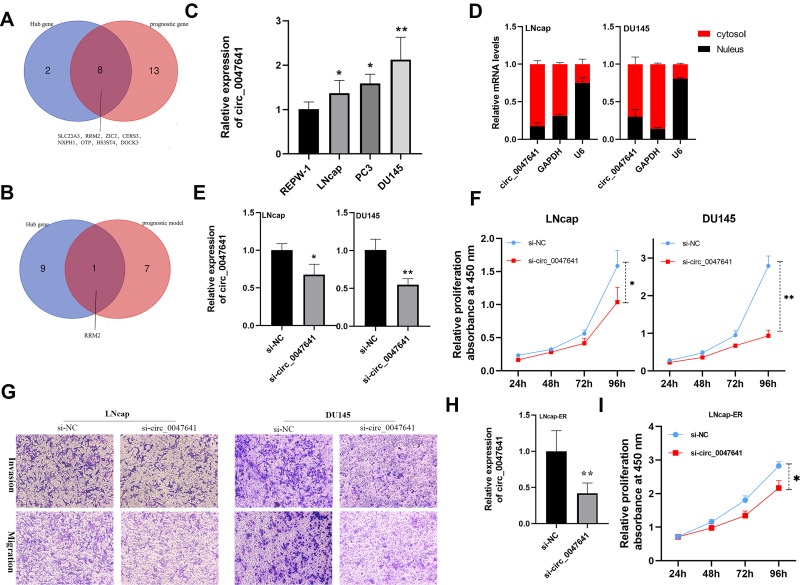
Figure 8.
Identification and characterization of hsa_circ_0047641 in prostate cancer (PCa). (A) Venn Diagrams showing the overlap of Hub genes and prognosis-related target genes. (B) Venn Diagrams showing the overlap of Hub genes and target genes in prognostic signature. (C) qRT-PCR was performed to examine the expression levels of hsa_circ_0047641 in normal prostate cells (REPW-1) and different PCa cell lines (LNcap, PC3, DU145). (D) The cellular distribution of hsa_circ_0047641 was analyzed by cellular RNA fractionation assays and qRT-PCR in LNcap and DU145 cells. U6 was being used as a nucleus marker and GAPDH as a cytosol marker. (E) qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression level of hsa_circ_0047641 in LNcap and DU145 cells after treatment with si-circ_0047641 or si-NC. (F) CCK-8 assays showed that silencing circ_0047641 suppressed the proliferation of LNcap and DU145 cells. (G) Transwell migration and invasion assays showed that silencing circ_0047641 suppressed the migration and invasion capabilities of PCa cells. (H) qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression level of hsa_circ_0047641 in enzalutamide resistance LNcap (LNcap-EnzR) cells after treatment with si-circ_0047641 or si-NC. (I) CCK-8 assays showed that silencing circ_0047641 suppressed the proliferation of LNcap-EnzR cells. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Abbreviations: si-circ_0047641, siRNA against circ_0047641. si-NC, siRNA for negative control