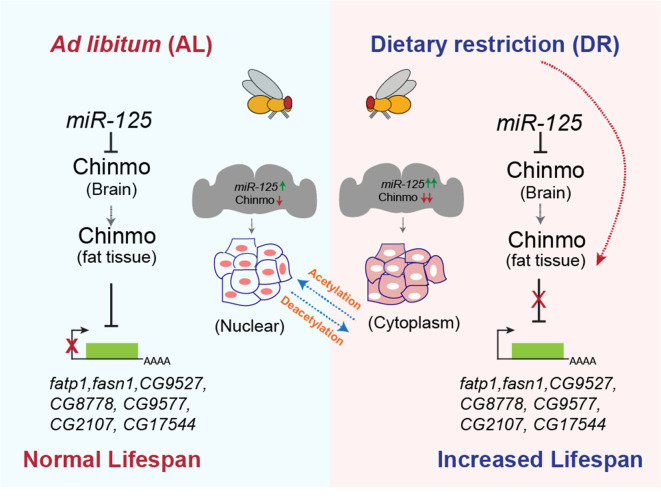
Figure 9. miR-125 regulates DR-dependent lifespan extension by post-transcriptionally silencing chinmo.
Proposed model summarizing the mechanism by which miR-125 and chinmo regulate lifespan extension by DR. miR-125 targets chinmo mRNA in the brain under AL and DR conditions. In the adult fat tissue, Chinmo transcriptionally represses genes involved in fat metabolism. DR-mediated cytoplasmic relocalization of Chinmo in the fat tissue relieves transcriptional repression of genes involved in fat metabolism, thus increasing lifespan.