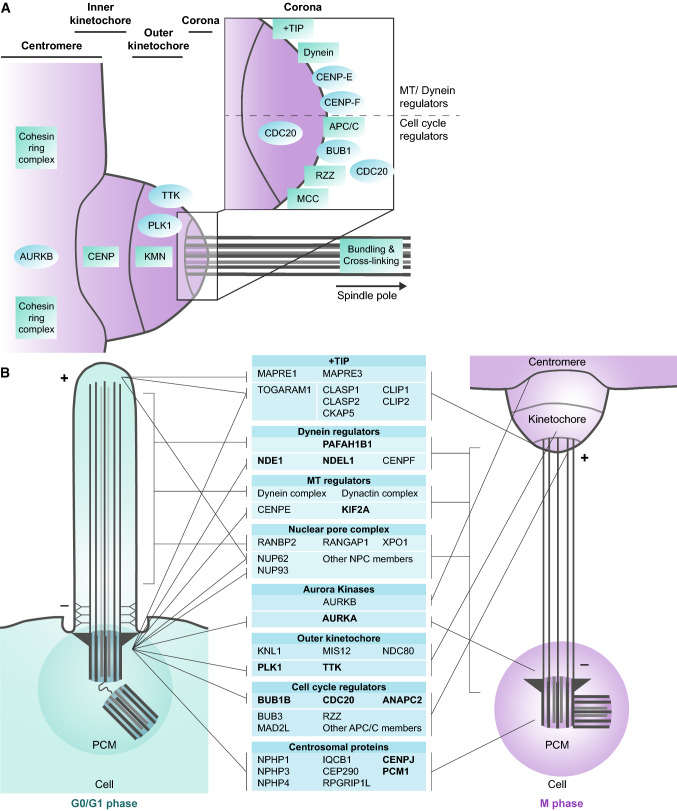
Fig. 3.
Conservation between the cilia, kinetochores and spindle poles. a Schematic representation of the kinetochore, and the key proteins present in each part of this structure. Individual proteins are indicated as circles (blue), protein complexes as squares (green). The MTs are docked onto the outer kinetochore. The corona contains many different proteins and protein complexes (inset), which either affect MT and dynein organization or cell cycle regulation. The MTs are bundled and crosslinked to withstand the high mechanical forces between the kinetochores and spindle poles prior to and upon segregation of the sister chromatids. b Many proteins and protein complexes are conserved between the cilia, kinetochores and spindle poles. Proteins that have been confirmed to play a role in ciliary resorption are marked (bold). The proteins are sorted per module and their organization in the two structures seems to be dependent on the MT organization, from minus at the bottom to plus at the top