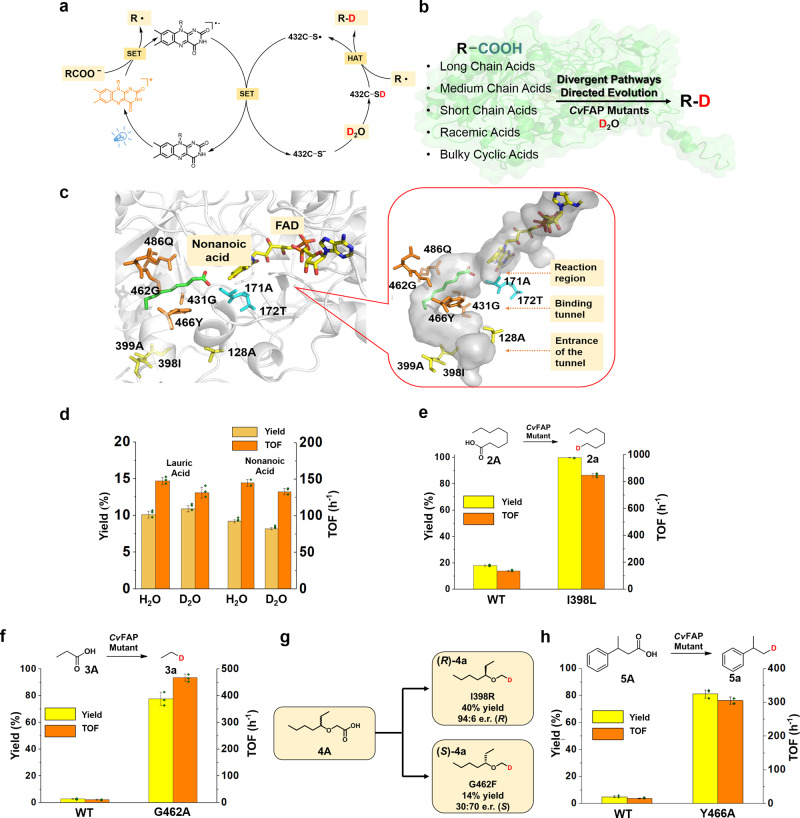
Fig. 1. Design of CvFAP-catalyzed decarboxylative deuteration and divergent directed evolution of CvFAP.
a Proposed mechanism of CvFAP-catalyzed decarboxylative deuteration. b Design of divergent directed evolution of CvFAP toward various substrates. c Docking result with nonanoic acid (green) and selected hot positions for protein engineering (PDB:5NCC)49, FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) and some representative residues located at the entrance of the substrate pocket (yellow), binding region (orange) and reaction region (cyan) are represented by sticks with different colors. d The influence of kinetic isotope effect on the reaction activity. e The comparison of yields and TOF between WT-CvFAP and the best mutant (I398L) for the medium chain acid. f The comparison of yields and TOF between WT-CvFAP and the best mutant (G462A) for the short chain acid. g The enantiodivergent decarboxylative deuteration catalyzed by I398R and G462F mutants, respectively. h The comparison of yields and TOF between WT-CvFAP and the best mutant (Y466A) for bulky cyclic acid. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.