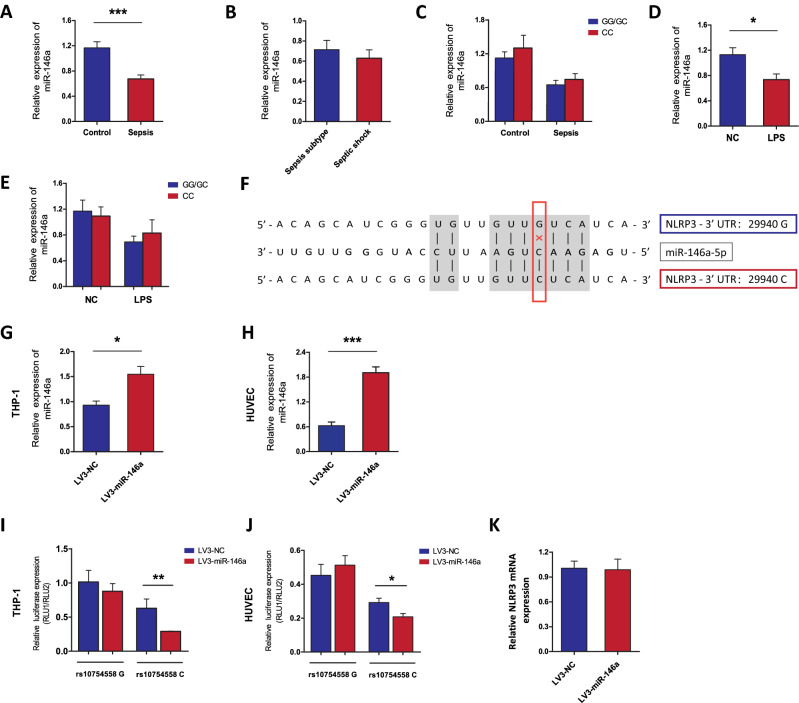
Figure 6.
The NLRP3-29940G>C is a gain-of-function alteration causing suppression of NLRP3 expression via altering miR-146a-5p binding. (A–C) The miR-146a expression in septic patients (n = 50) and healthy controls (n = 50) with different rs10754558 polymorphism; (D, E) PBMCs isolated from 50 healthy subjects with different rs10754558 genotypes were stimulated with 500 ng/mL of LPS (n = 25) or PBS (n = 25) in vitro, and then miR-146a expression was detected; (F) Bioinformatics predicted that the rs10754558 G-to-C mutation was located at the binding site between 3′UTR of NLRP3 and miR-146a-5p; (G, H) HUVECs and THP-1 cells were infected by LV3-miR-146a (miR-146a overexpression) or LV3-NC, and the infection efficiency of LV3-miR-146a was determined by qRT-PCR analysis; (I, J) The effect of miR-146a on the transcriptional activities of rs10754558 G>C in HUVECs and THP-1 cells were determined by dual-luciferase report assays; (K) The effect of miR-146a on NLRP3 expression in THP-1 cells was determined by qRT-PCR analysis. Bar graphs indicate the mean ± SEM for a minimum of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.