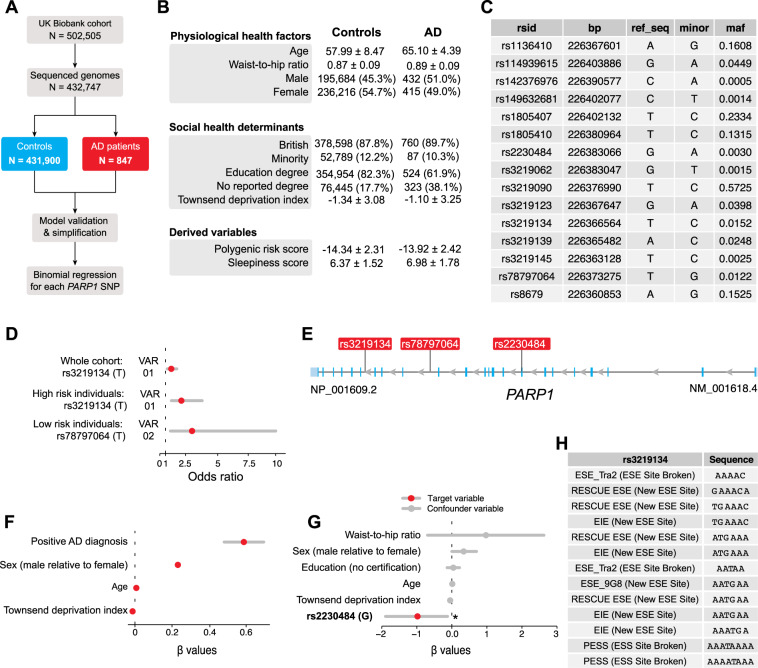
Fig. 5. Gene variants in human PARP1 alter the risk and severity of AD.
A Workflow of the analysis. Out of a total of 502,505 UK Biobank participants, 432,747 patients who contained genomic data were analysed. B Descriptive statistics of the UK Biobank cohort that was analysed. Either the number of participants in each category and their percentage with respect to the total cohort or the mean and standard deviation are shown. A full table of summary characteristics is available in Supplementary Table 3. C Table of the 15 SNPs in PARP1 present in our cohort. The SNP name (rsid), base position (bp), reference sequence (ref_seq), minor allele (minor) and minor allele frequencies are shown. This information was extracted from the NCBI database. D Odds ratios of the significant SNP in PARP1 associated with the risk of AD and their respective 95% confidence intervals. The odds ratios are calculated with respect to the allele shown in parentheses using individual binomial models that accounts for covariates. Only the significant SNPs are shown. Statistics of all 15 SNPs analysed are shown in Supplementary Table 4. E Genomic location of the PARP1 SNPs that are significantly associated with AD risk (VAR01 and VAR02) as well as sleepiness in AD (VAR03, explained in the next figure). F AD patients have a higher risk of sleepiness. β values with respect to the sleepiness score are calculated using a linear regression, after accounting for age, sex, social deprivation (Townsend deprivation score), education and obesity. Only the significant associations are shown. The numeric values of this model are in Supplementary Table 7. G β values of the model containing the significant SNP (rs2230484) that is associated with differences in sleepiness in the subset of patients with AD. Statistics of all 15 SNPs investigated are shown in Supplementary Table 8. H Theoretical impact of the SNP rs3219134 (T to C) on the gene-splicing efficiency. ESE Exonic Splicing Enhancers, ESS Exonic Splicing Silencer, EIE exon-identity elements.