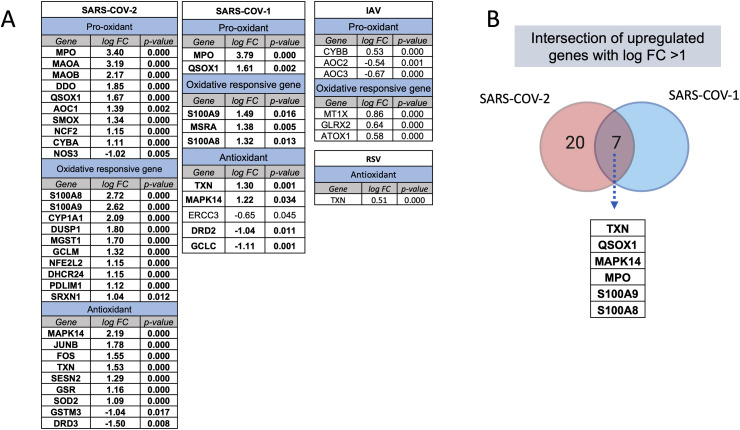
Fig. 5.
Expression of oxidative stress genes during SARS-COV-2 and other viral infections. The number and intensity of gene upregulation were higher during SARS-COV-2 infection compared to other respiratory viral infection. (A) Upregulation of oxidative stress genes during different respiratory infections. The difference in gene expression of case and controls is provided as fold change. (B) Intersection of upregulated oxidative signatures in coronavirus infections; SARS-COV-1 and SARS-COV-2. The following datasets were used; GSE17156 (n = 17 IAV vs n = 17 controls), GSE17156 (n = 20 RSV vs n = 20 controls), GSE1739 (n = 10 SARS-COV-1 vs n = 4 controls), and EGAS00001004503 (n = 39 COVID-19 vs n = 10 controls). For all analyses, p < 0.05 was considered significant. IAV, influenza A virus; RSV, Respiratory syncytial virus.