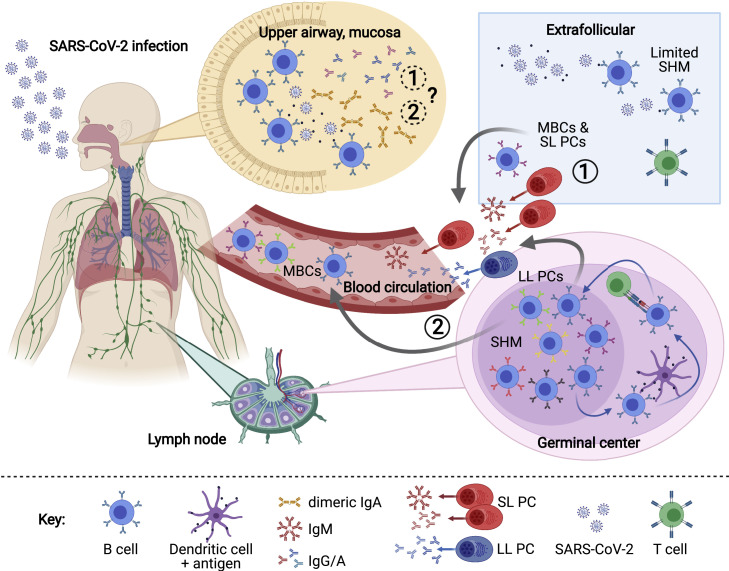
Figure 1.
Overview of the humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2
SARS-CoV-2 antigen recognition initiates a cascade of immune responses, including the activation of naive B cells. Activated B cells can differentiate rapidly into extrafollicular, short-lived plasma cells (SL PCs) and memory B cells (MBCs) with low rates of somatic hypermutation (SHM) (1), or they can enter germinal centers of secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, where they undergo rounds of SHM and affinity maturation, resulting in long-lived plasma cells (LL PCs) and MBCs (2). Antibody-secreting plasma cells and MBCs can enter the blood and (potentially) mucosa, where they help to fight viral infection and protect from reinfection. LL PCs also transit to the bone marrow and potentially to other anatomical sites. Schematic created with biorender.com.