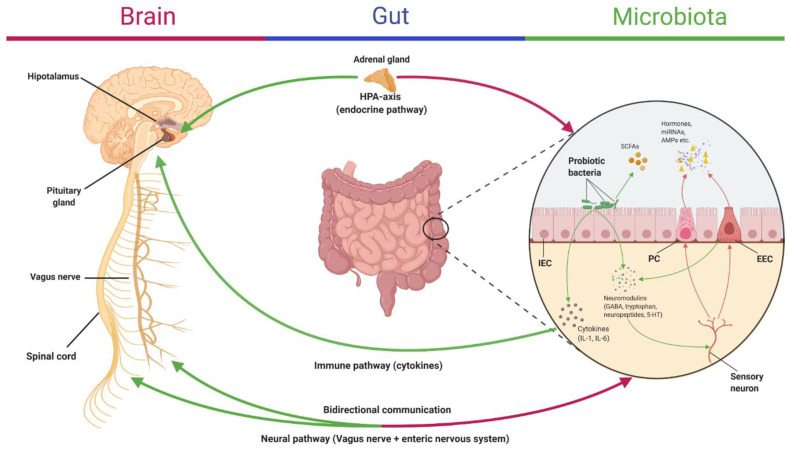
Figure 2.
Microbiota–gut–brain axis communication pathways. In this figure, the main bidirectional communication routes between the brain and the gut microbiota are illustrated. The most studied interaction paths between the brain and the gut microbiota are represented by the endocrine pathway, consisting mainly of the HPA axis and enteric endocrine cells (EECs), the neural pathway, that includes the vagal nerve and the enteric nervous system, and the immune pathway, which is mediated via cytokines. Abbreviations. HPA-axis: Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis; IEC: Intestinal epithelial cell; EEC: Enteric endocrine cell; PC: Paneth cell; SCFA: Short-chained fatty acid; IL: Interleukin; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; 5-HT: Serotonin; AMP: Antimicrobial peptide; miRNA: MicroRNA. Figure created with BioRender.com.