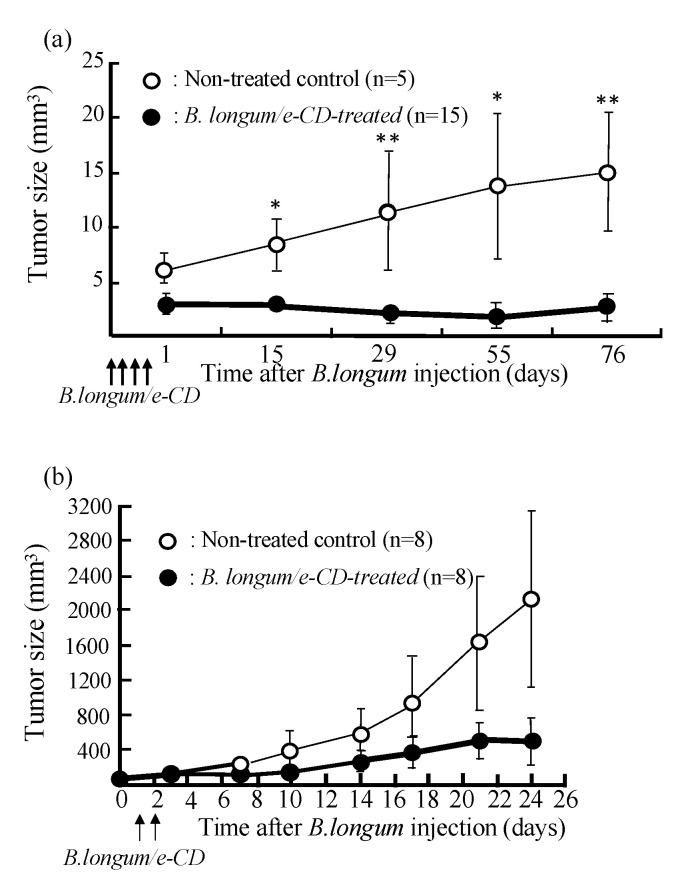
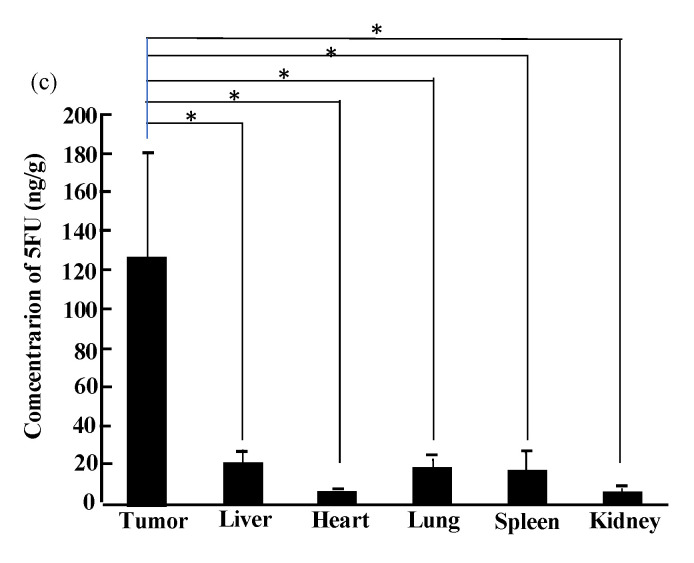
Figure 2.
Anti-tumor effects of i.v. injected cytosine deaminase of Escherichia coli (e-CD)-transformed Bifidobacterium longum (B. longum/e-CD) combined with oral 5-fluorocytosine (5FC). (a) Comparison of tumor volumes of non-injected rats (n = 5) with those of B. longum/e-CD i.v. injected rats (n = 15). Rats bearing 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary tumors received i.v. B. longum/e-CD and 500 mg/kg/day 5FC. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. (b) Anti-tumor assessment of B. longum/e-CD in nude mice transplanted with KPL-1 human mammary tumor cells. Tumor-bearing nude mice (n = 8) were given a dose of transformed bacteria cells i.v. (5.9 × 109 c.f.u./mouse), followed by oral 5FC for 21 days. (c) Measurement of 5-fluorouracil (5FU) concentration in various tissues in rats bearing MRMT-1 mammary gland carcinoma. Rats were given B. longum/e-CD at 1.1 × 1010 c.f.u./rat i.v. and 5FC by intragastric gavage for 4 days starting on day 4 after bacterium injection. The concentration of 5FU in normal tissues and tumor tissues was measured. Rats given 5FC without injection of B. longum/e-CD were used as controls. * p < 0.05. These figures were adopted from a previous study [11,36].