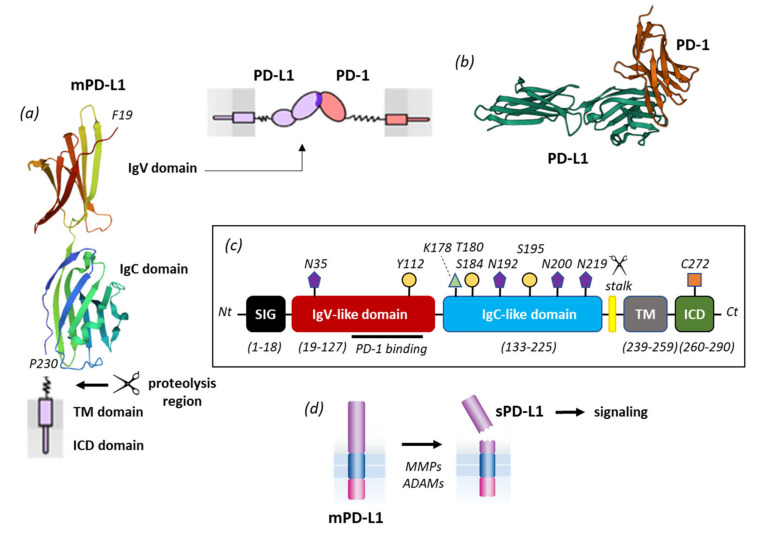
Figure 3.
PD-L1 primary structure and processing. (a) mPD-L1 with its IgV domain (which interacts with PD-1) and IgC domain linked to the transmembrane domain (TM) via a short flexible stalk. The TM domain is connected to the intracellular (ICD) domain. The molecular model of PD-L1 derives from the crystal structure of the free protein (PDB access code 3BIS). (b) Model of PD-1 interacting with PD-L1 via its IgV domain. (c) Primary structure of mPD-L1 with the different domains and sites of post-translational modifications (N-glycosylation at N35, N192, N200 and N219; phosphorylation at Y112, T180, S184, S195, ubiquitination at K178 and palmitoylation at C272). Proteolytic cleavage generally occurs within a short stalk region situated between the IgC and TM domains. (d) Representation of mPD-L1 shedding by different proteases (MMPs, ADAMs) to release a soluble form of PD-L1, which plays a role in cell signaling.