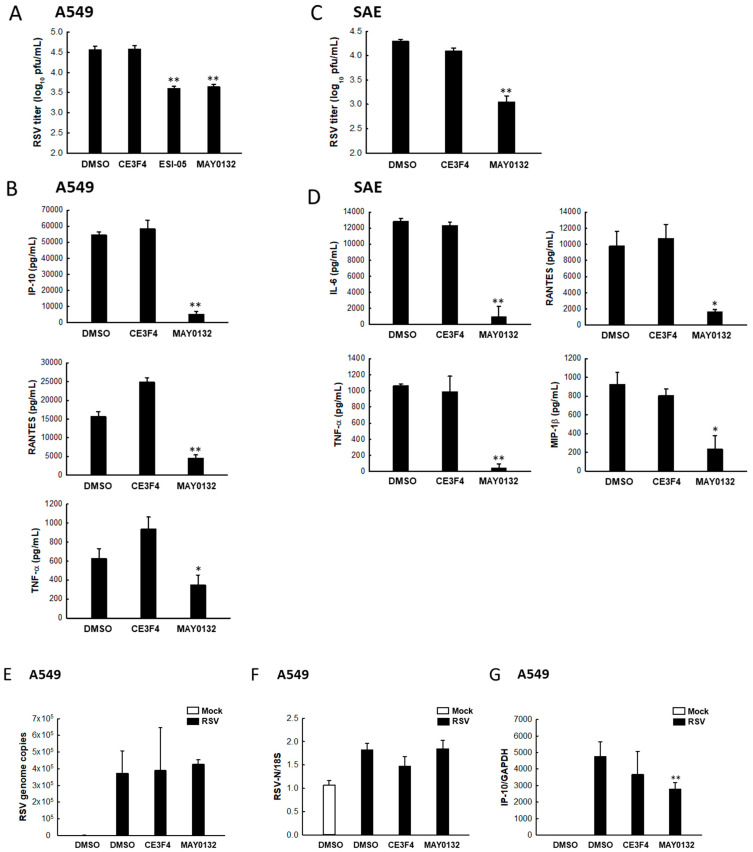
Figure 5.
The impact of EPAC2 on RSV infection. (A,B) A549 cells in triplicate were infected with RSV at an MOI of 1. After 2 h p.i., cells were treated with DMSO, 20 μM CE3F4, 20 μM ESI-05, or 20 μM MAY0132. At 15 h post-treatment, (A) total viruses were collected, and viral titer was determined by immunostaining using an anti-RSV antibody. (B) The supernatant was collected, and diluted or undiluted cytokines/chemokines were measured by Bio-Plex. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01, relative to the DMSO-treated group. (C,D) SAE cells were infected with RSV and treated with the indicated drugs as described in (A). At 15 h post-treatment, (C) virus titration was determined. ** p < 0.01, relative to the DMSO-treated group. (D) Cytokines/chemokines of SAE cells were also measured by Bio-Plex. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01, relative to the DMSO-treated group. (E–G) A549 cells in triplicate were infected with RSV and treated with drugs as described in (A). At 4 h post-treatment, total RNA was extracted and subjected to qRT-PCR to measure RSV genome copies (E), N gene expression (F), and IP-10 transcription (G). DMSO-treated mock infection was used as a negative control for DMSO-treated RSV infection. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01, relative to the DMSO-treated and RSV-infected group.