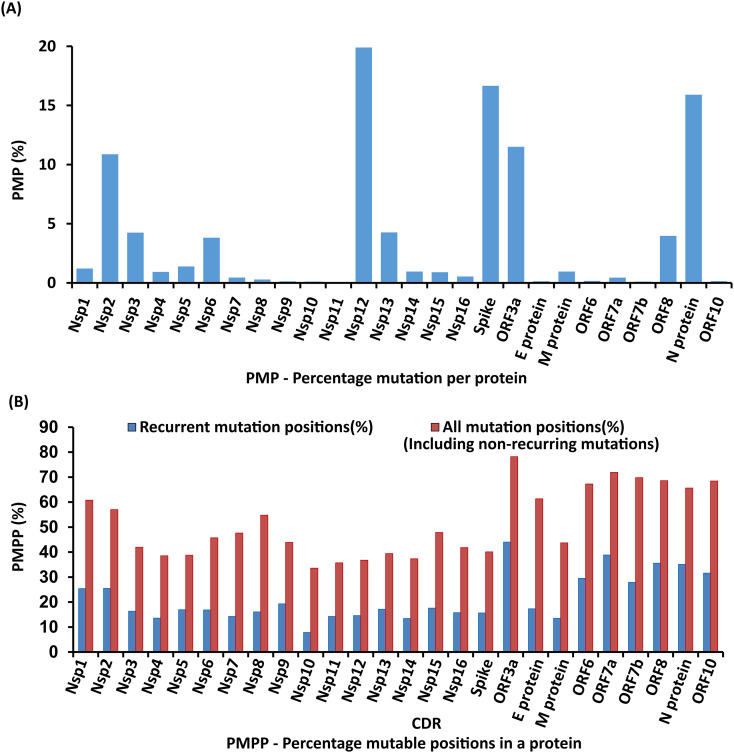
Fig. 1.
Bar diagram illustrating the mutation susceptibility (%) of 26 proteins (See Supplementary Table S1 for functions). (A) Considering the mutation count from individual proteins, the mutation susceptibility (Eq. (2)) falls in the following order: Nsp12 > Spike >N protein > ORF3a > Nsp2 > Nsp13 > Nsp3 > ORF8 > Nsp6 > Nsp5 > Nsp1 > Nsp14 > M protein > Nsp4 > Nsp15 > Nsp16 > Nsp7 > ORF7a > Nsp8 > ORF6 > ORF10 > E protein > Nsp9 > ORF7b > Nsp10 > Nsp11. (B) When the mutation position count is considered, the mutation susceptibility (Eq. (3)) falls in the following order: ORF3a > ORF7a > ORF8 > N protein> ORF10 > ORF6 > ORF7b > Nsp2 > Nsp1 > Nsp9 > Nsp15 > E protein > Nsp13 > Nsp5 > Nsp6 > Nsp3 > Nsp8 > Nsp16 > Spike > Nsp12 > Nsp7 > Nsp11 > Nsp4 > M protein > Nsp14 > Nsp10.