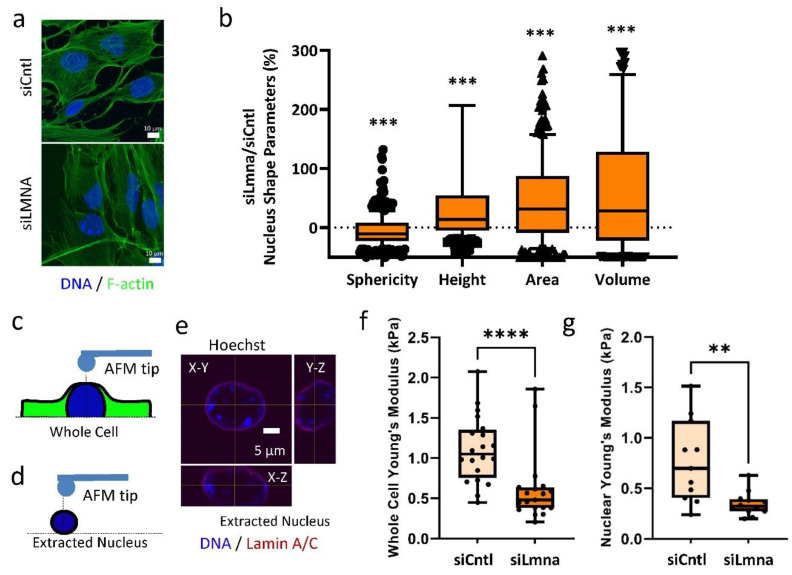
Figure 1.
siRNA depletion of lamin A/C weakens the nuclear elastic modulus in MSCs: (a) Confocal Image of F-actin (phalloidin, green) and nucleus (Hoechst, blue). Scale bar: 10 µm. (b) Nuclear sphericity decreased by 8% in MSCs treated with Lamin A/C specific siRNA (siLmna) compared to MSCs treated with a non-specific control siRNA (siCntl) (p < 0.05, n = 342). Nuclear area of siLmna treated cells showed a 32% increase when compared to siCntl (p < 0.05, n = 342). Nuclear volume siLmna treated cells increased by 31% compared to siCntl (p < 0.05, n = 342). When compared to the nuclear height of siCntl MSCs, siLmna treated cells had increased nuclear height of 12% (p < 0.05, n = 342). (c) Schematic of AFM probe tip testing whole cell Young’s modulus in live MSCs. (d) Depiction of AFM probe tip testing live extracted nucleus. (e) Confocal image of extracted nucleus depicting its orthogonal views from X-Y, X-Z, Y-Z planes (Hoechst, blue; Lamin A/C, Red) Scale bar: 5 µm. (f) Whole cell Young’s modulus of the siLmna group was 45% lower when compared to the siCntl group (p < 0.0001, n = 16). (g) Young’s modulus of extracted live nucleus in siLmna MSCs remained 55% lower when compared to siCntl MSCs (p < 0.01, n = 13). Results are presented as mean ± STD. Group comparisons were made via non-parametric Mann Whitney tests. p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 against control.