Figure 1.
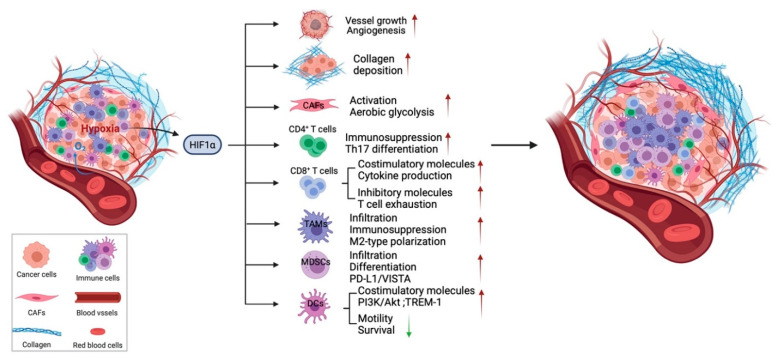
Hypoxia affects the tumor stroma. In addition to multiple effects of hypoxia on cancer cells, hypoxia through HIF-1α signaling regulates the tumor stroma, including tumor vasculature, ECM, CAFs, and immune cells. HIF signaling is essential for vessel growth and maturation. Hypoxia also regulates CAF functions and leads to increased secretion of ECM components. However, the effects of hypoxia on each type of immune cell are complex and, in some cases, controversial. In general, hypoxia results in infiltration of immunosuppressive cells such as TAMs and Tregs and regulates the differentiation, phenotype polarization, as well as the cytotoxic function of immune cells to create an immunosuppressive environment. Hypoxia contributes to tumor progression, metastasis, and compromises the efficacy of standard of care therapy and immunotherapy in numbers of indications. Green arrow pointing down, decreased; red arrow pointing up, increased.