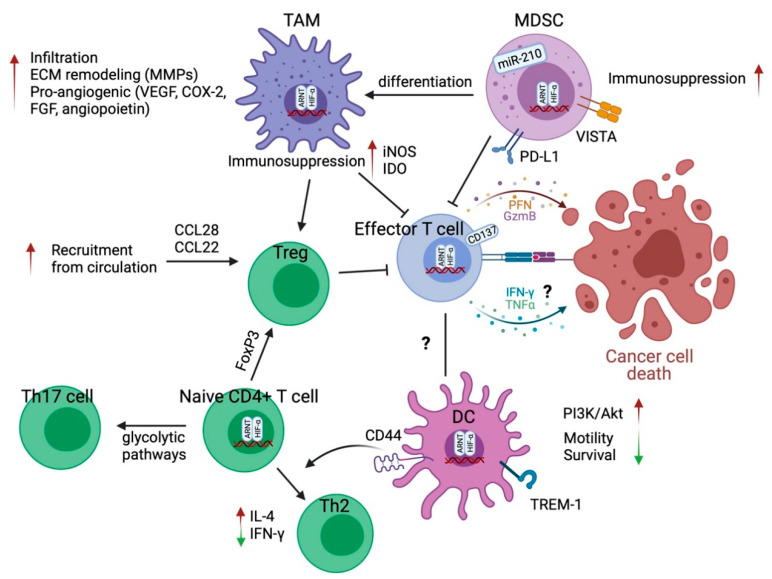
Figure 2.
HIF signaling effects on immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. HIF signaling, mainly HIF-1α generally promotes an immunosuppressive microenvironment. In TAMs and MDSCs, HIF-1α contributes to their infiltration and enhanced suppressive capacity on effector T cells. HIF-1α can also stimulate a proangiogenic phenotype of TAMs and TAM-mediated ECM remodeling. The hypoxic microenvironment stimulates the secretion of cytokines and chemokines from tumor cells or TAMs to recruit Tregs, further limiting effector T cell function. There is conflicting evidence of HIF signaling in determining T cell fate. HIF-1α has been demonstrated to induce or inhibit differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th17 T cells or Tregs. HIF-1α signaling also exhibits controversial effects on effector T cell function and the migration and maturation of DCs. The effect of hypoxia on DC and T cell interaction is an area ripe for further investigation. Green arrow pointing down, decreased; red arrow pointing up, increased.