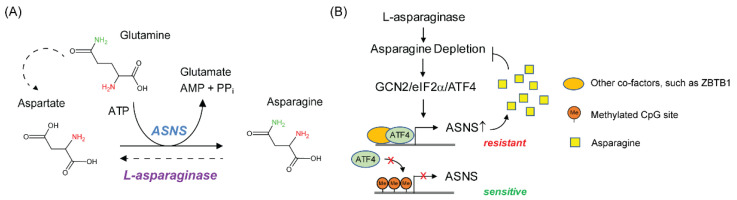
Figure 1.
Asparagine de novo biosynthesis in driving L-asparaginase resistance. (A) ASNS catalyzes asparagine biosynthesis by using glutamine, aspartate and ATP. In proliferating mammalian cells, most aspartate is synthesized de novo by using oxaloacetate and glutamate as substrates. Since glutamate is produced through glutamine deamination, which can be further deaminated to fuel the TCA cycle to generate oxaloacetate, glutamine is the major carbon and nitrogen donor for aspartate biosynthesis [56]. Catabolism of asparagine to aspartate by L-asparaginase has not been reported in mammalian cells. (B) Asparagine depletion by L-asparaginase activates GCN2 pathway, leading to ATF4 accumulation, which turns on ASNS. As a result, cells synthesize more asparagine to mitigate the stress. However, ATF4 cannot be recruited to the ASNS promoter unless it is demethylated.