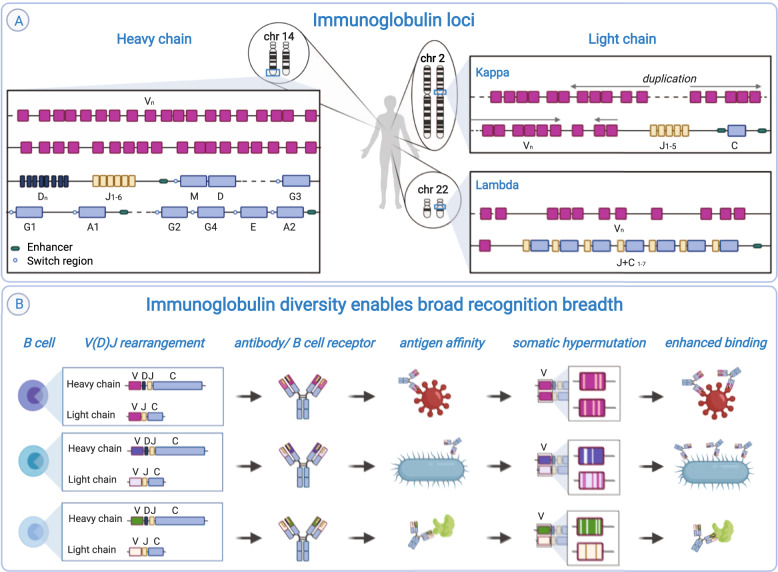
Fig. 1. Immunoglobulin loci can give rise to antibodies and BCRs with various antigen specificity.
A In humans, the main immunoglobulin loci are located on chromosomes 14 (heavy), 2 (kappa) and 22 (lambda). Each of the main Ig loci contains clusters of V, J and C genes, and the heavy locus also contains a cluster of D genes. The organisation of genes within each locus is different. The production of a functional transcript requires V(D)J recombination. This figure is schematic only and does not show all genes present in the loci. B Different V(D)J combinations, as well as various pairings of heavy and light chain, produce a diverse set of antibodies/BCRs with a variety of paratopes with the capacity to recognise different antigens. The binding capacity of antibodies can be further enhanced by somatic hypermutation, which introduces point mutations in mutational hotspots of the V genes.