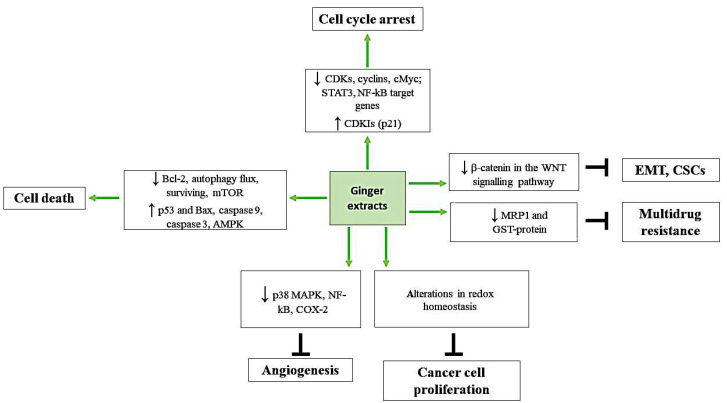
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram showing main molecular targets of ginger derivatives. The natural compound participates in the cell cycle arrest by inhibiting the expression of cyclins, CDKs, and levels of STAT3, NF-kB target genes, and by activation of cell cycle check points and increased expression of p21. Moreover, by increasing Bax/Bcl-2 ratio outburst of cytochrome C, activating AMPK, and by decreasing autophagy flux and survivin expression, ginger derivatives provoke cancer cell death. They participate in the alteration of redox homeostasis, which stops cancer cell proliferation. By blocking activation of p38 MAP kinase (p38 MAPK) and NF-kB, ginger derivatives inhibit COX-2 expression and as a result block angiogenesis. Ginger extracts decrease β-catenin in the WNT signaling pathway, which leads to the inhibition of gene transcription, involved in EMT and CSCs, and, additionally, downregulate MRP1 and GST-protein expression, involved in multidrug resistance.