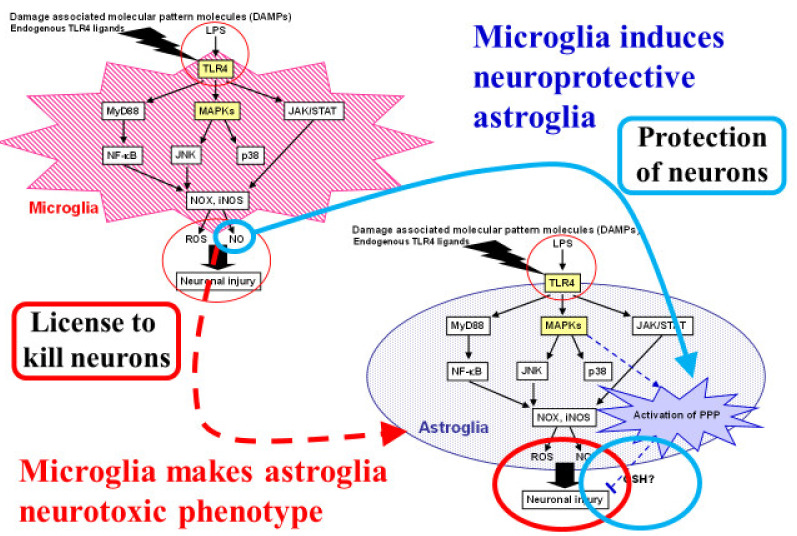
Figure 5.
Dual roles of microglia that induce both proinflammatory-neurotoxic and anti-inflammatory-neuroprotective astrocytes. Astrocytes are known to play neurotoxic roles in ischemic stroke as well as neurodegenerative diseases. Microglia induce neurotoxic astrocytes through proinflammatory responses induced by toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 activation. Reactive oxygen species (ROSs) and nitric oxide (NO) also act as neurotoxic molecules that can cause neuronal injury. We focused on the neuroprotective roles of astrocytes through their high glycolysis activity and the pentose-phosphate pathway (PPP) against oxidative stress. Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a natural TLR4 ligand, induce ROS and NO production in microglia. We found that NO released from microglia activated astroglial PPP flux through the Kelch-like enoyl-CoA hydratase-associated protein 1 (Keap1)/nuclear factor erythroid 2 p45 subunit-related factor 2 (Nrf2) system. Namely, the NO-induced nitrosylation of Keap1 residues released Nrf2 from Keap1, allowing Nrf2 to act as a transcription factor in an in vitro model of cultured rodent microglia and astroglia.