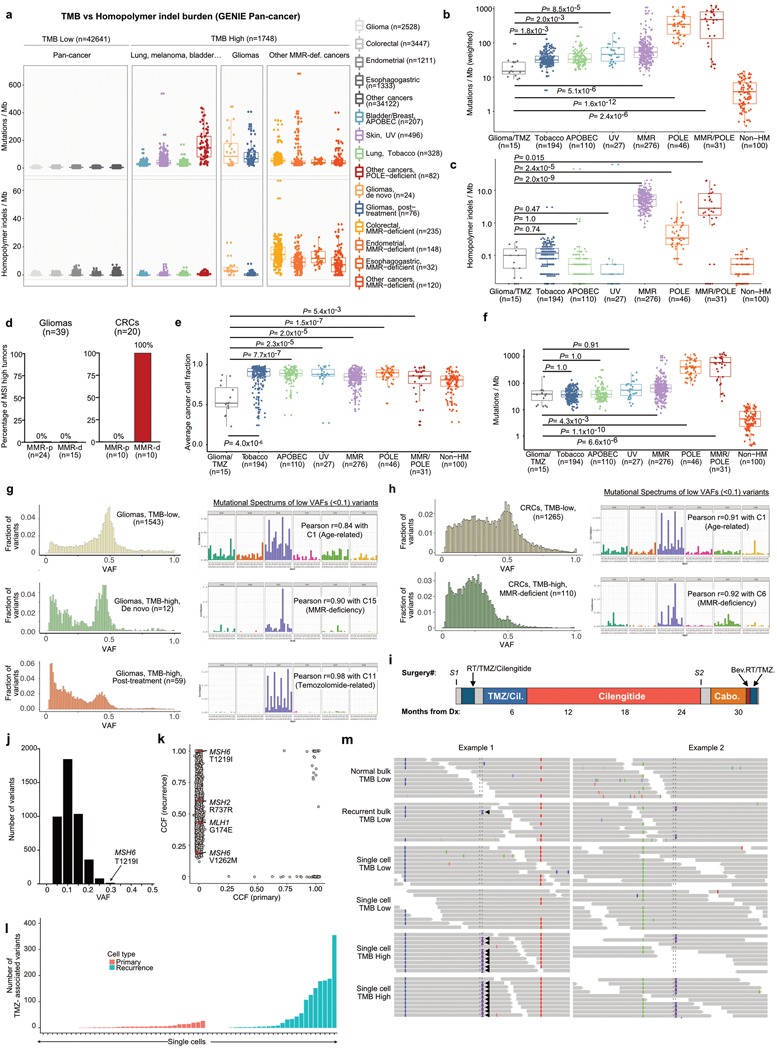
Extended Data Figure 11. Molecular Characteristics of Hypermutated Gliomas.
a, Pan-cancer analysis of TMB and homopolymer indel burden in the GENIE dataset (n = 44,389). Tumour samples from the GENIE dataset (v6.1) were analysed for mutational and homopolymer indel burden. Statistical comparisons between groups are provided in Supplementary Table 6. b, TMB in hypermutated gliomas (post-treatment) versus MMR-deficient cancers and other hypermutated cancers from the TCGA and Wang et al. 4 exome datasets (n = 798). Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test with Bonferroni correction. c, Pan-cancer analysis of the homopolymer indel burden in hypermutated gliomas (post-treatment) versus MMR-deficient cancers and other hypermutated cancers from the TCGA and Wang et al. 4 exome datasets (n = 798). d, Results of MSI analysis using the standard pentaplex assay in glioma (n = 39) and CRC samples (n = 19) according to MMR status (MMR-d, MMR deficient; MMR-p, MMR-proficient). e, Pan-cancer analysis of cancer cell fractions in hypermutated gliomas (post-treatment) versus MMR-deficient cancers and other hypermutated cancers from the TCGA and Wang et al. 4 exome datasets (n = 798). Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test with Bonferroni correction. f, Weighted TMB in hypermutated gliomas (post-treatment) versus MMR-deficient cancers and other hypermutated cancers from the TCGA and Wang et al. 4 exome datasets (n = 798). The weighted TMB was calculated by weighing each individual mutation to its cancer cell fraction. Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test with Bonferroni correction. g, Distribution of VAFs (left) and mutation spectrum analysis of low-allelic frequency variants (<0.1, right) in TMBlow gliomas (n = 1,543, top), de novo hypermutated gliomas with MMR deficiency mutational signature (n = 12, middle), and post-treatment hypermutated gliomas (n = 59, bottom) from the DFCI-Profile dataset. h, Distribution of VAFs (left) and mutation signature analysis of low-allelic frequency variants (<0.1, right) in TMBlow CRCs (n = 1,265, top) and TMBhigh CRCs with MMR deficiency mutational signature (n = 110, bottom) from the GENIE dataset. i, Clinical timeline for the patient with hypermutated glioblastoma with an MSH6(T1219I) mutation in whom bulk and single-cell WGS was performed. j, Distribution of VAFs of mutations in the recurrent bulk sample. The median VAF in the recurrent sample was 0.11. The MSH6(T1219I) mutation had the 18th-highest VAF out of 4,350 coding mutations. k, Cancer cell fractions (CCFs) of mutations in the primary and recurrent tumour bulk samples. Each dot represents a coding mutation. The horizontal and vertical axes are estimated clonal frequency for each mutation in the primary and recurrent samples, respectively. Mutations of the four main MMR genes are depicted in red. l, Mutational spectra in 35 cells from the primary tumour (orange) and 28 from the recurrent tumour (green) submitted to scWGS sequencing (1×). Mutational signature analysis showed a strong contribution of mutational signature 11 in hypermutated cells from the recurrent tumour. m, Representative IGV plots (n = 2 distinct genomic segments for each sample) of microsatellite insertions in the normal (TMB low) and recurrent (TMB high) bulk samples and recurrent TMB low (n = 2) and TMB high (n = 2) single cells. Solid arrowheads represent microsatellite insertions phased with a flanking heterozygous SNP allele. Open arrowheads represent microsatellite insertions for which the reads do not reach the flanking heterozygous SNP allele. Both hypermutated single cells showed multiple phased microsatellite insertions consistent with a true somatic microsatellite mutation. In general, a few reads with similar microsatellite insertions correctly phased with the same flanking heterozygous SNP allele were found in the recurrent bulk, but not in the normal bulk or non-hypermutated cells. For a–c, e, f, biological subgroups were identified on the basis of mutational burden, dominant signature and histology. For b, c, e, f, 100 non-hypermutated samples were randomly selected as controls. For all box plots: boxes, quartiles; centre lines, median ratio for each group; whiskers, absolute range, excluding outliers. RT, radiation therapy; Cil, cilengitide; Cabo, cabozantinib; Bev, bevacizumab.