FIGURE 1.
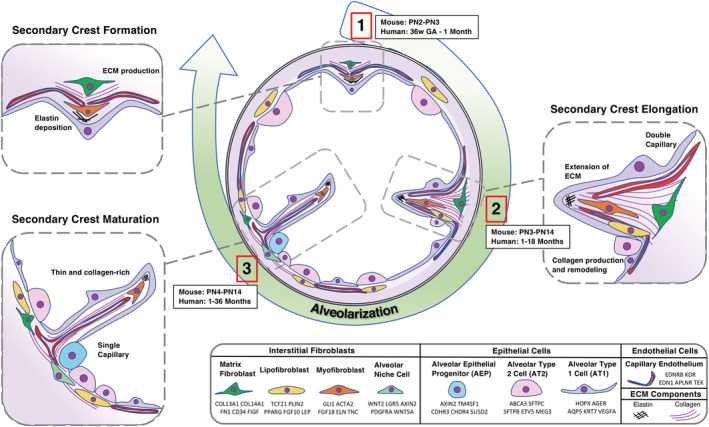
Interstitial fibroblasts and their role in alveolar septation and epithelial niche formation. Illustrations of mesenchymal subtypes in their spatial and temporal contributions to alveolarization. Three key stages of alveolarization are arranged in a clockwise fashion in the center of the illustration. (1) Secondary crest formation occurs in mice between PN2 and PN3 and in humans between 36 weeks' gestational age (GA) and 1 month. (2) Secondary crest elongation occurs in mice between PN3 and PN14 and in humans between 1 and 18 months. (3) Secondary crest maturation occurs in mice between PN4 and PN14 and in humans between 1 and 36 months. Major events, such as elastin deposition during primary septum formation, are labeled in the respective panels. The spatial location of each cell type is reflected, such as the myofibroblast that resides at the septal tip and the lipofibroblast sitting adjacent to the AT2 cell. Signature gene expression of each cell type, identified by developmental studies and scRNA‐seq, are given in the figure legend
