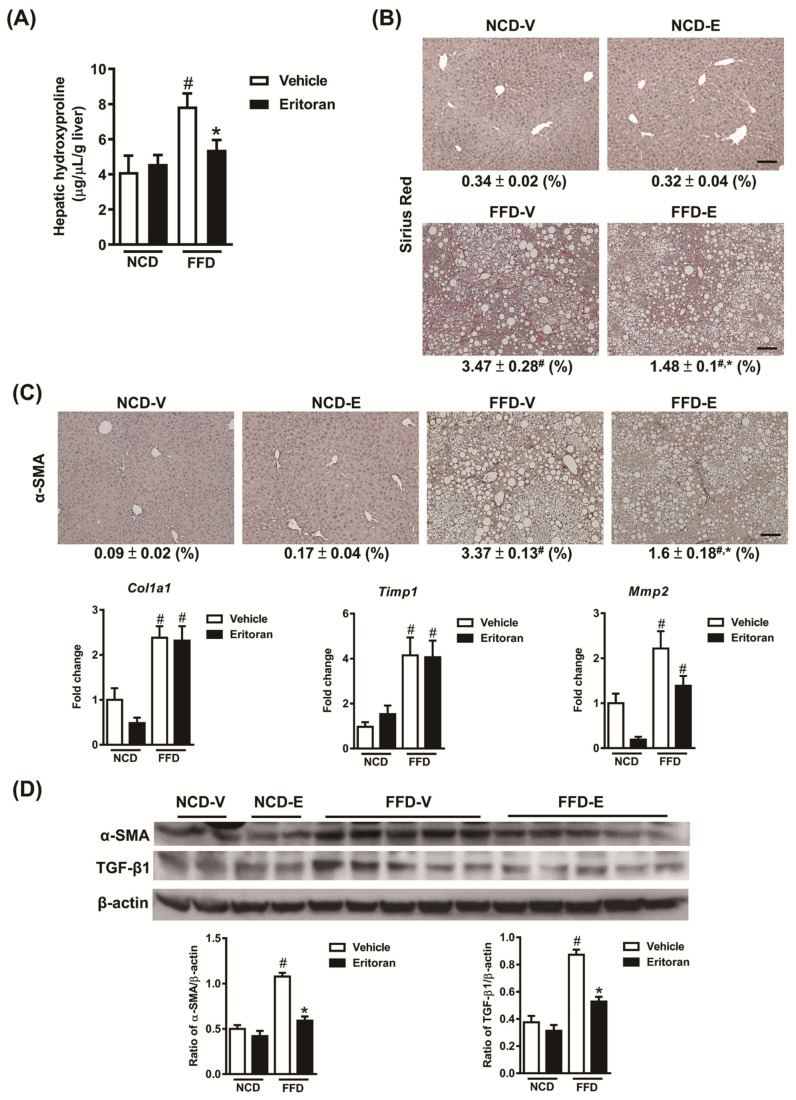
Figure 3.
Eritoran attenuated liver fibrosis in the mice fed a fast-food diet. (A) Hepatic hydroxyproline levels. (B) Sirius Red staining of the liver sections and quantification of the positively stained areas (%). Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) Immunohistochemical staining for α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) of the liver sections and quantification of the positively stained areas (%), as well as the hepatic transcript levels of collagen 1α1 (Col1a1), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (Timp1) and matrix metalloproteinase 2 (Mmp2). Scale bar = 100 μm. Tissue sections from all the mice were stained and quantified (means ± SEM). (D) Western blotting of α-SMA and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in the livers. Each four samples from the NCV-V/NCD-E groups and 9–10 samples from the FFD-V/FFD-E groups were used for Western blot quantification. NCD-V/NCD-E: The mice fed a normal chow diet (NCD) were injected with a vehicle (NCD-V, n = 6) or eritoran (NCD-E, n = 6); FFD-V/FFD-E: the mice fed a fast-food diet (FFD) were injected with a vehicle (FFD-V, n = 10) or eritoran (FFD-E, n = 9); # p < 0.05 vs. NCD-V; * p < 0.05 vs. FFD-V.