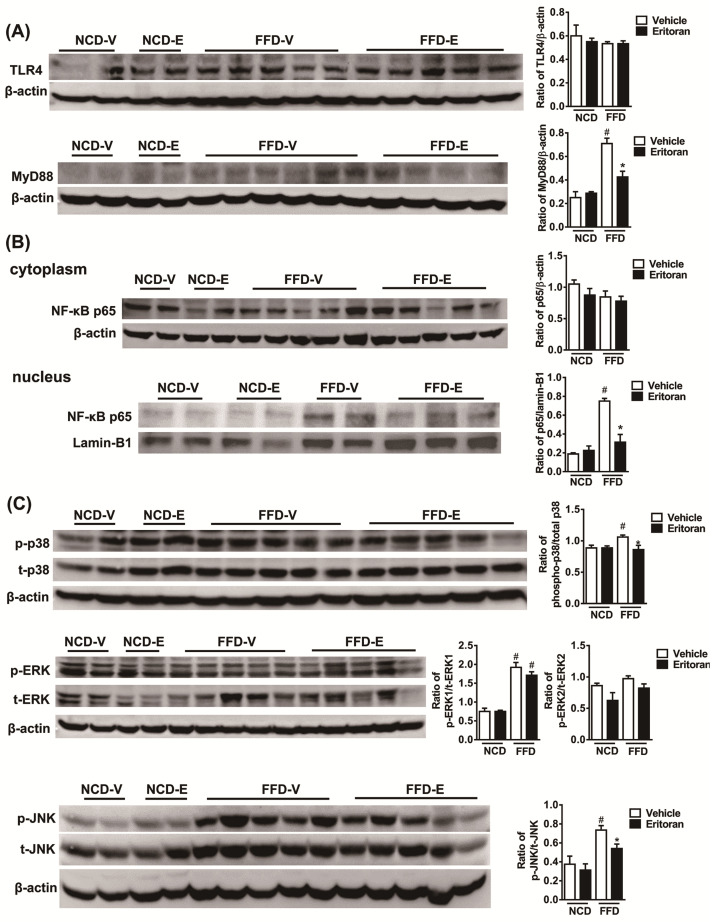
Figure 5.
Eritoran suppressed the hepatic TLR4 downstream signaling pathway in the mice fed a fast-food diet. Western blot analysis and quantification of (A) TLR4 and myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88); (B) cytoplasmic and nuclear NF-κB p65; (C) phosphorylated and total p38 (p/t-p38), extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (p/t-ERK1/2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p/t-JNK) expression in the livers. NCD-V/NCD-E: the mice fed a normal chow diet (NCD) were injected with a vehicle (NCD-V, n = 6) or eritoran (NCD-E, n = 6); FFD-V/FFD-E: the mice fed a fast-food diet (FFD) were injected with a vehicle (FFD-V, n = 10) or eritoran (FFD-E, n = 9). Four samples from each of the NCV-V/NCD-E groups and 9–10 samples from the FFD-V/FFD-E groups were used for Western blot quantification; # p < 0.05 vs. NCD-V; * p < 0.05 vs. FFD-V.