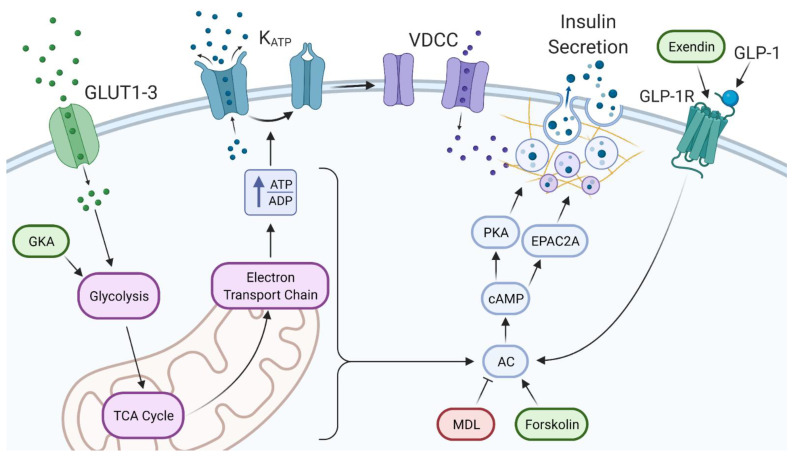
Figure 6.
The triggering and amplifying pathways of insulin secretion in extreme glucose. (Left) Glucose enters the beta cell and is metabolized, causing an increase in the ATP to ADP ratio. ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) close, causing membrane depolarization, the opening of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCC), and insulin secretion. (Right) GLP-1 from alpha cells or exendin stimulate beta-cell GLP-1 receptors which stimulate AC. Additionally, various metabolites produced from glucose metabolism can stimulate AC. Increased production of cAMP stimulates PKA and EPAC2A, causing increased insulin secretion by various mechanisms. Ovals indicate points of stimulation (green) or inhibition (red) for pharmacological agents used in these studies.