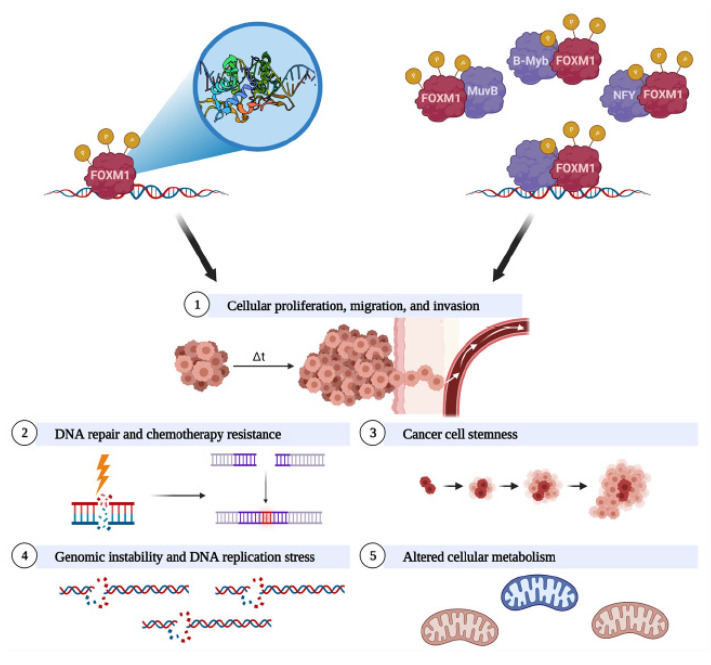
Figure 4.
The oncogenic functions of FOXM1 in ovarian cancer. FOXM1 transactivates genes by binding to gene enhancers and promoters, either directly through its DNA binding domain (DBD) or indirectly by interacting with other transcription factors (B-Myb, MuvB, and NFY). Through these two mechanisms, FOXM1 has been shown to promote several oncogenic phenotypes in ovarian cancer, including: (1) cellular proliferation, migration, and invasion; (2) DNA repair and chemotherapy resistance; (3) cancer cell stemness; (4) genomic instability and DNA replication stress; (5) altered cellular metabolism. Figure created with BioRender.com.