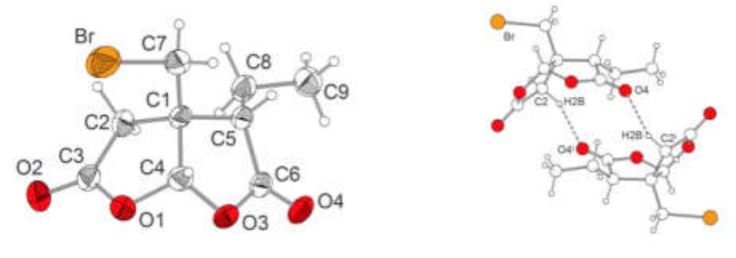
Figure 2.
Molecular structure of compound 13 in the crystal. Thermal ellipsoids with a 50% probability. H atoms with arbitrary radius. C–H…O hydrogen bonds between two symmetrically related enantiomeric molecules. Selected bond lengths (pm) and angles (°): C(1)–C(2) 154.1(4), C(1)–C(4) 154.6(4), C(1)–C(5) 154.6(4), C(1)–C(7) 152.1(4), C(2)–C(3) 149.6(4), C(3)–O(1) 135.9(4), C(3)–O(2) 119.3(4), C(4)–O(1) 141.7(3), C(4)–O(3) 141.7(4), C(5)–C(6) 151.5(4), C(5)–C(8) 153.0(4), C(6)–O(3) 136.4(4), C(6)–O(4) 119.4(4), C(7)–Br 195.4(3), C(8)–C(9) 151.9(4), C(2)–C(1)–C(4) 102.1(2), C(3)–C(2)–C(1) 105.7(3), O(1)–C(3)–C(2) 110.5(2), C(3)–O(1)–C(4) 111.3(2), O(1)–C(4)–C(1) 108.6(2), C(5)–C(1)–C(4) 103.0(2), C(6)–C(5)–C(1) 103.9(2), O(3)–C(6)–C(5) 110.3(2), C(6)–O(3)–C(4) 111.8(2), O(3)–C(4)–C(1) 107.6(2), C(1)–C(7)–Br 112.4(2). Hydrogen bond C(2)–H(2B)–O4i: C(2)…O(4)i 316.7, C(2)–H(2B)–O(4)i 125.98; symmetry operator i: –x, -y+1, -z+1.