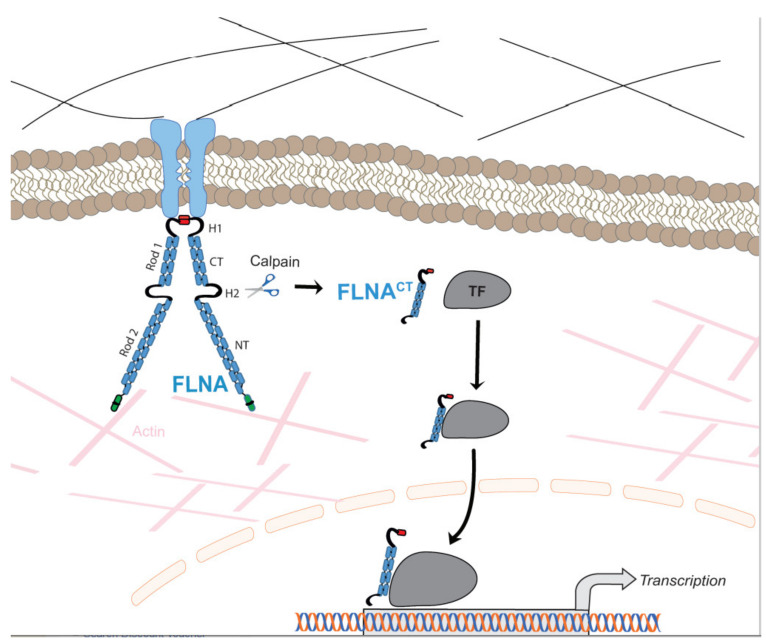
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the regulation of function of transcriptional factors (TF) by FLNA. Membrane-bound FLNA mediates extracellular signals to the cytoskeleton. FLNA interacts with multiple TF in a cell-specific manner in the cytoplasm. Increased calpain protease activity cleaves membrane-bound FLNA releasing the FLNACT, which is translocated to the nucleus together with TF. As part of the transcriptional complex, FLNACT can also bind to promoter regions of target genes. Thus, FLNACT increases the transactivation function by facilitating translocation to the nucleus and/or nuclear retention and/or by working as a transcriptional coactivator.