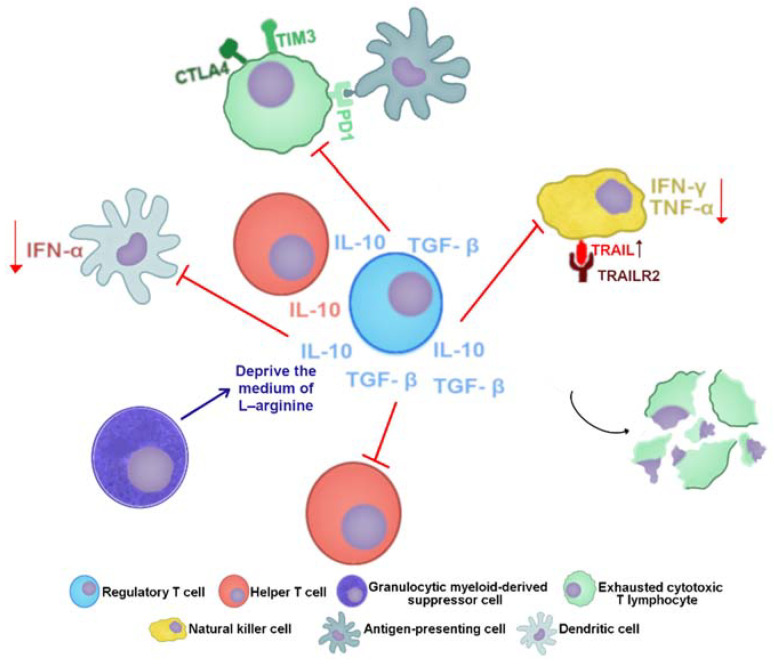
Figure 5.
The induction of tolerant state during chronic hepatitis B. T cells are induced to an exhausted state; the secretion of IL-10 and TGF-β by Treg cells inhibits the activity of immune cells such as DCs and NK cells. CTLs express higher levels of TRAILR2, which makes them susceptible to die by interacting with cells such as NK cells, which express higher levels of TRAIL in CHB patients. There is also metabolic regulation conducted by gMDSCs by consuming the L-arginine available in the medium. Cells and their secreted cytokines are colored the same. Trunked red lines indicate inhibitory effects, and red arrows indicate a reduction of secretion. Abbreviations: IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRAILR2; or TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor 2; CTLA4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; TIM3, T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain-3; PD1, programmed cell death protein 1.